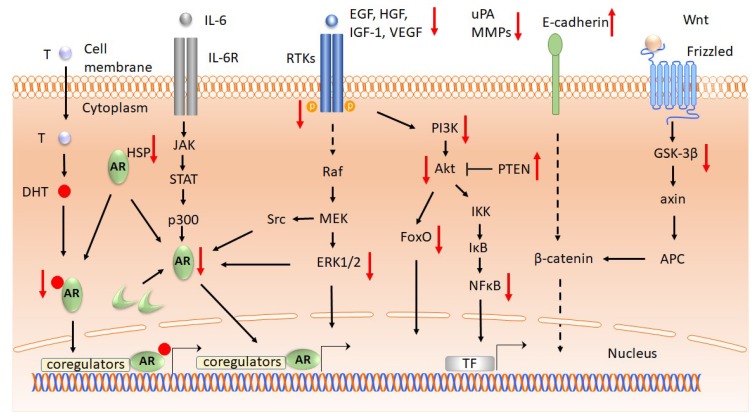
Figure 3.
The effects of polyphenols on signaling pathways in prostate cancer. In the canonical pathway ARs are activated by DHT binding. AR can be transactivated in the absence of DHT through different signaling pathways: increased activity of RTK or interleukin receptors and their signaling pathways, modifications of the coregulatory proteins, or constitutively activated AR [115,126]. Ligand binding to RTK activates PI3K/Akt kinases, which trigger the activation of IKK. This pathway induces phosphorylation of IκB, resulting in its ubiquitylation and proteasome-mediated degradation. NF-κB is maintained in the cytoplasm by the interaction with IκB, and degradation of IκB activates NF-κB, which in turn is enabled to enter the nucleus and activate the genes involved in cell survival [127,128]. For simplification, the canonical pathway of NF-κB activation that takes place through the members of tumor necrosis factor receptors or interleukin receptors is omitted from the figure [129]. Similarly, the canonical pathway of PI3K/Akt signaling is not presented. Polyphenols might modulate the levels of signaling molecules in prostate cancer by decreasing or increasing their levels. Polyphenols downregulate AR (quercetin, genistein, resveratrol, EGCG), HSP90 (genistein), IGF-1 (apigenin), EGFR (curcumin, resveratrol), HER2 (resveratrol), ERK (apigenin, gallic acid, EGCG), phosphorylated PI3K (apigenin, curcumin, resveratrol), phosphorylated Akt (apigenin, CAPE, gallic acid, resveratrol), FoxO (apigenin), NF-κB (apigenin, curcumin, gallic acid, EGCG), GSK-3β (CAPE), VEFG (apigenin, genistein, quercetin, EGCG), uPA (apigenin), MMPs (apigenin, gallic acid, EGCG, genistein) and upregulate PTEN (resvetratol) and E-cadherin (apigenin). Legend: AR, androgen receptors; T, testosterone; DHT, dehydrotestosterone; HSP, heatshock protein; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; Raf, rapid accelerated fibrosarcoma protein; MEK, mitogen activated protein kinase, kinase; ERK1/2, extracellular signaling regulate d kinase; EGF, epidermal growth factor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; Akt, Ak thymoma protein-kinase (protein kinase B); NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IκB, inhibitor of κB; IKK, IκB kinase; FoxO, forkhead box O protein; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Wnt, wingless/integrated ligand; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; TF, transcription factors; CAPE, caffeic acid phenethyl ester; EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate; upregulation (red ↑), downregulation (red ↓).