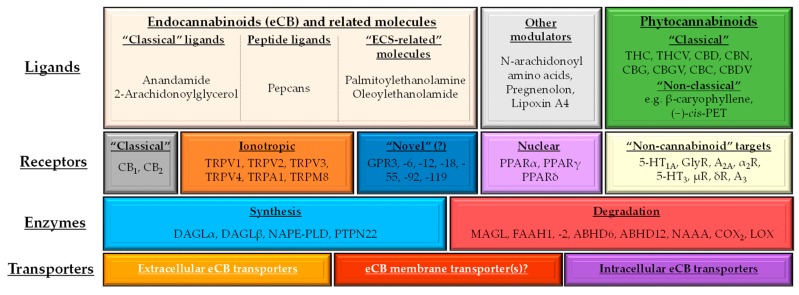
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the (endo)cannabinoid system (ECS) and its putative connections to other signaling systems. Depending on how we choose to limit the definition, the number of the putative ligands as well as that of the possible targets increases dramatically; therefore, on the figure, we only summarize the most important ones. Each ligand possesses a unique molecular fingerprint, i.e., the ability to concentration-dependently activate/antagonize/inhibit a selected group of possible targets. Obviously, all these actions are highly context-dependent (e.g., they are influenced by the relative expression of the potential targets in the given tissue, the concentration of the substance), resulting in characteristic, and in some cases even opposing biological responses. Although the classical, lipophilic eCBs definitely require inter- and intracellular carriers, relatively little is known about these transporter systems. Intracellular eCB transporters may include fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), whereas FABP4, albumins, HSP70 and extracellular vesicles [61,62] are likely to be involved in their intercellular transport [63]. With respect to FAAH1 and -2 it is important to note that only scarce evidence is available about the expression and functionality of the latter. Intriguingly, FAAH2 is not expressed in mice and rats, but shares substrate spectrum of FAAH1 (however, it has inferior affinity towards AEA and N-acyl taurines). Conventional FAAH-inhibitors can inhibit its activity [48], and its missense polymorphism (A458S) may lead to psychiatric disorders (anxiety, mild learning disability) [64]. Later in the text, except when stated otherwise, by mentioning “FAAH”, we refer to “FAAH1”. 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor; A2A and A3: adenosine 2A and 3 receptors; ABDH6 and -12: α/β-hydrolase domain containing 6 and 12; CBC: (−)-cannabichromene; CBD: (−)-cannabidiol; CBDV: (−)-cannabidivarin; CBG: (−)-cannabigerol; CBGV: (−)-cannabigerovarin; CBN: (−)-cannabinol; (−)-cis-PET: (−)-cis-perrottetinene; COX2: cyclooxygenase-2; DAGL: diacylglycerol lipase; eCB: endocannabinoid; FAAH: fatty acid amide hydrolase; GPR: G protein-coupled receptor; LOX: lipoxygenase; MAGL: monoacylglycerol lipase; NAAA: N-acylethanolamine hydrolyzing acid amidase; NAPE-PLD: N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PTPN22: protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22; THC: (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol; THCV: (−)-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin; TRP: transient receptor potential.