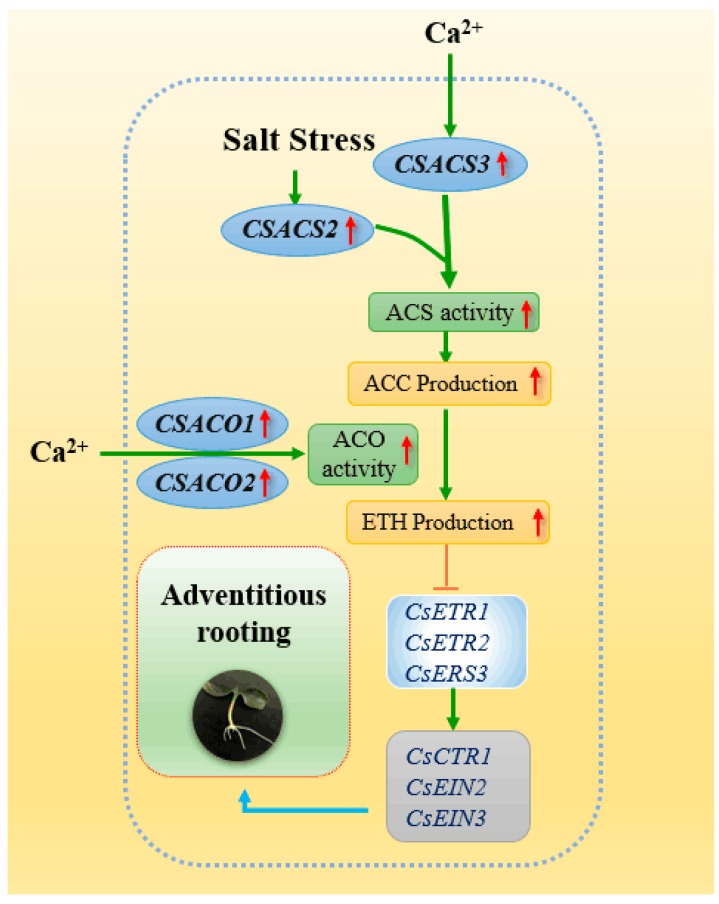
Figure 8.
Schematic model of the signaling networks involving Ca2+ and ethylene during adventitious rooting in cucumber under salt stress. Ca2+ could promote the development of adventitious root under salt stress through regulating the activities and transcriptional levels of ACS and ACO enzyme to trigger endogenous ethylene accumulation. Meanwhile, the receptors and downstream components of ethylene signaling pathway could be regulated by Ca2+ during adventitious rooting under salt stress. T bars, inhibition.