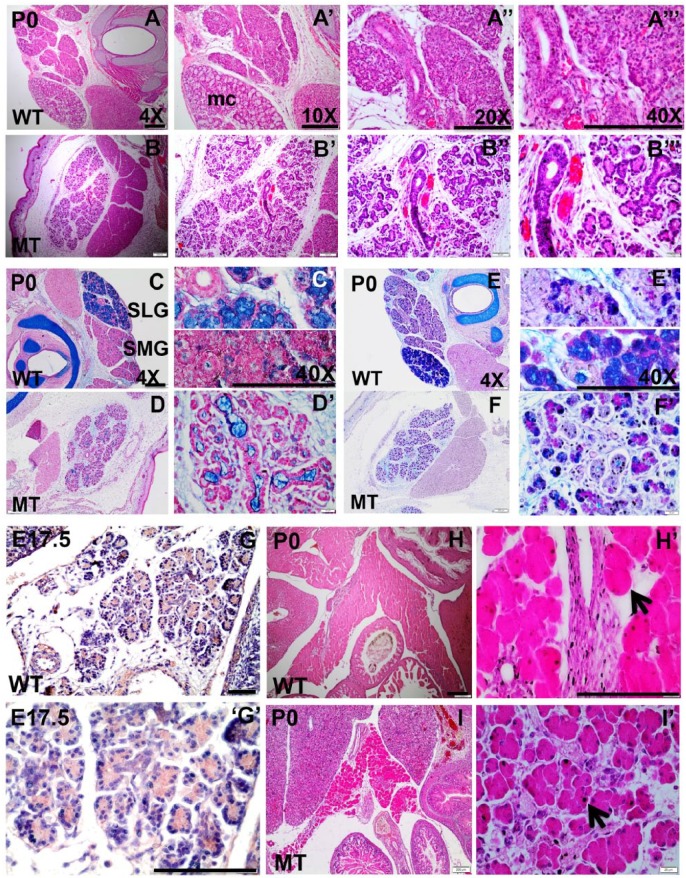
Figure 3.
Histologic studies to detect phenotypic abnormality in Irf6-null salivary gland and pancreas. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (A, B series), alcian blue and nuclear fast red staining (C, D series), and alcian blue and periodic acid–Schiff staining (E, F series) were performed on submandibular gland (SMG) and sublingual gland (SLG) of wild-type (WT) and Irf6-null tissues at postnatal day 0 (P0). Expression of IRF6 (G series) is detected by IHC in pancreas, and H&E staining (H, I series) was performed in WT and Irf6-null pancreatic sections. H&E staining visualizes the SMG and SLG of the salivary gland in WT where SLG is recognized by the whitish cytosol of mucous acini (mc). Ducts and serous acini appear compact with single organized lumen (A′′–A′′′), while the ductal and acinar cells are disorganized in the mutant and SLG is not distinguished (B–B′′′). Alcian blue and nuclear fast red staining shows a remarkable reduction in mucin and mucous cell (mc) formation (blue-stained cells) in Irf6-null SLG and SMG (D, D′) versus WT (C, C′). Alcian blue and periodic acid–Schiff staining of SMG and SLG in WT differentiates glycoprotein substances as purple, acidic mucins as blue, neutral mucins as magenta, mixed mucous as bluish purple, and nuclei as dark blue (D, D′). Staining shows a decrease in acidic mucins in Irf6-null SMG and SLG (F, F′). IRF6 is expressed in pancreas in cytosol of acinar cells at embryonic day (E17.5; G, G′). H&E staining showed abnormal morphology, disorganized acinar cells (black arrow in I′), and wide interstitial spaces among acini in Irf6-null pancreas at P0 (I, I′) as compared with WT littermates (H, H′, black arrow). Scale bars are 150 μm.