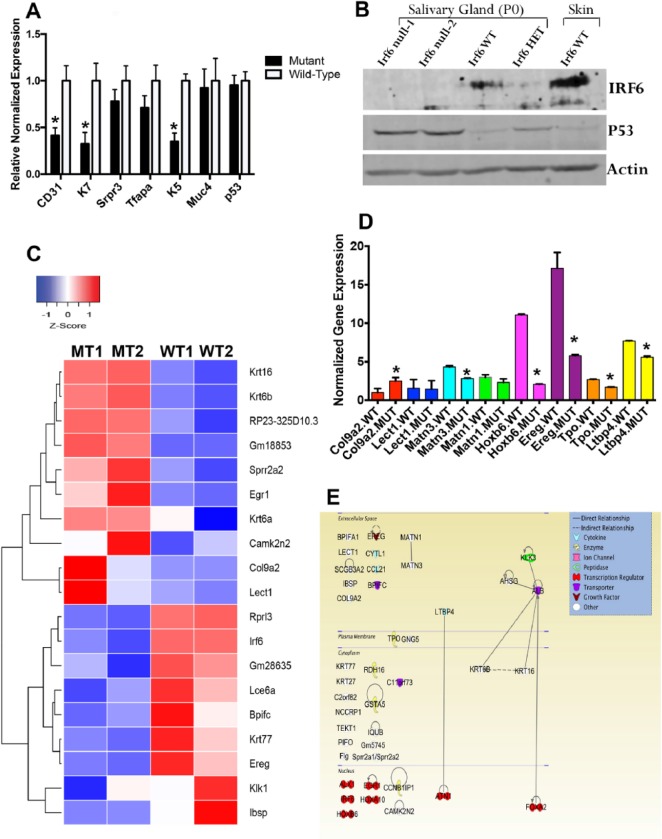
Figure 5.
Analysis of altered gene expression in submandibular gland of wild-type (WT) and Irf6-null mice (mutant type [MT]). At embryonic day 17.5 (E17.5), normalized expression of multiple genes shows significant reduction in CD31, K7, and K5 expression, while no change is observed in mRNA of Srpr3, Tfap2a, Muc4, and p53 as compared with WT littermates (A). The values are the mean normalized expression, and the bars represent the standard deviation. Protein levels in Irf6-null, heterozygous, and WT submandibular salivary gland tissues were investigated by immunoblot assay. Skin tissue from WT pups was used as positive control and showed higher expression of IRF6 as compared with salivary glands (B). P0, postnatal day 0. The level of P53 protein was accumulated in Irf6-null versus heterozygote and WT tissues (B). Heat map of the top 19 significantly differentially expressed genes in Irf6-null embryos (MT1 and MT2) and their corresponding expression profile in WT littermate embryos (WT1 and WT2). Blue blocks represent genes that have decreased in expression, while red represents genes that have increased in expression. White represents no change in expression (C). Validation of 8 differentially expressed genes from RNA-Seq data in WT and Irf6 mutant salivary glands at E14.5 (D). The values are the mean normalized expression, and the bars represent the standard deviation. Asterisks represent statistical significance of Irf6-null samples versus WT, P < 0.05 (D). Ingenuity Pathway analysis of 41 differentially expressed genes from RNA-Seq data of Irf6-mutant SGs as compared with WT littermates was represented according to their connectivity and interactions at gene-gene and protein-protein levels (E). Several transmembrane transporter genes are involved. Five genes—that is, Ereg, Ltbp4, Matn1, Matn3, and Tpo—are involved in the EGF signaling pathway.