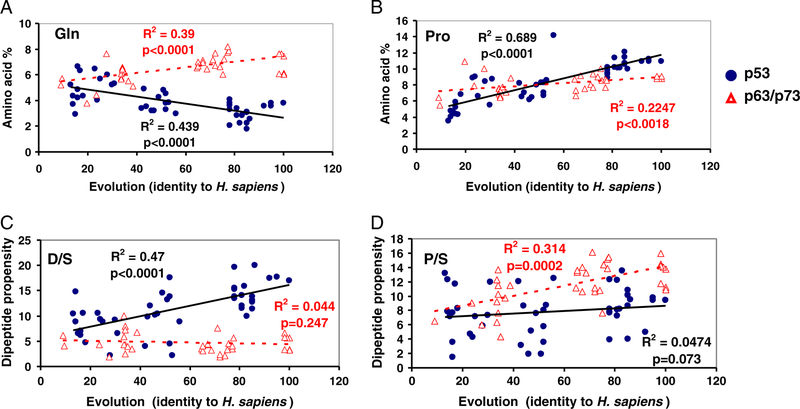
Fig. 1.
Evolution of amino acid and dipeptide composition in the p53/p63/p73 families. Some of the changes correlate with sequence identity to Homo sapiens. (A) and (B). While Gln composition decreased (A), Pro composition increased significantly (B); (C): The change of the D/S dipeptide propensity during evolution indicates that the D/S pair is positively selected in p53 (but not in p63/p73); (D). While dipeptide propensity of P/S in p53 did not correlate with p53 evolution, that in p63/p73 increased. Thus, both the most preferred dipeptide pairs in p53 (D/S) and in p63/p73 (P/S) were positively selected during evolution, for p53 and p63/p73 respectively.