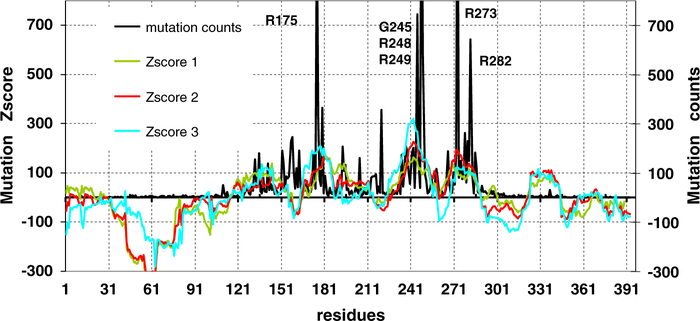
Fig. 5.
The simulated p53 mutation spectrum and the actual mutation frequencies counted from the IARC p53 mutation database Release R13. The number of hot spot positions was truncated from 750 for easy comparison with prediction (the actual counts are: 1152 for R175, 745 for G245, 1621 for R248, 573 for R249, 1551 for R273, 642 for R282). Several evolutionary factors may lower the mutation rate in the N- and C-termini (NC regions). In our simulation, on average the propensities of dipeptides gained from mutations are higher in the NC regions as compared to the core domain, indicating lower likelihood for mutations in the NC regions. The right Y-axis is the actual frequencies from IARC p53 mutation database Release R13.