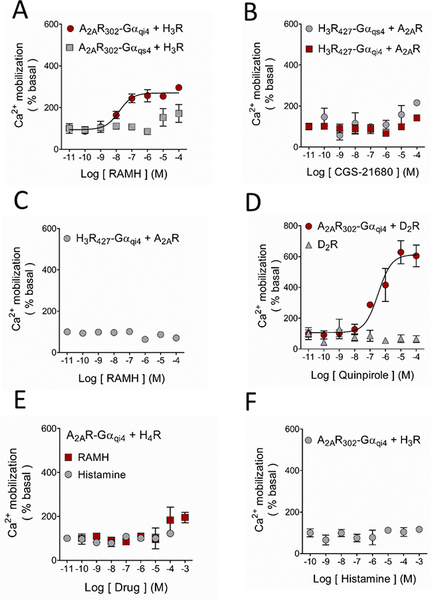
Figure 3.
Ligand modulation of the A2AR-H3R interaction in HEK-293 cells. Activation of the WT-H3R with its agonist RAMH led to functional complementation when co-expressed with the A2AR302-Gαqi4 but not with A2AR302-Gαqs4. B. Ca2+ mobilization was not observed when the WT-A2AR was co-transfected with the truncated H3R427-Gαqs4 or H3R427-Gαqi4, in accord with the incapability of the receptor to activate the chimeric proteins. C. As shown in Figure 1D, activation of the H3R427-Gαqi4 resulted in Ca2+ mobilization, and this response was prevented when it was co-expressed with the WT-A2AR, suggesting a preference of the H3R427-Gαqi4 to form heterodimers. D. The well-studied A2AR-D2R heterodimer was used as a positive control for these experiments. Activation of the D2R with increasing concentrations of the agonist quinpirole caused marked Ca2+ mobilization only when co-expressed with the chimeric A2AR302-Gαqi4. E. The histamine H4 receptor (H4R) as a negative control. No functional complementation was observed when the receptor was co-expressed with the A2AR302-Gαqi4, showing the specificity of the A2AR-H3R interaction. F. Functional complementation between the A2AR302-Gαqi4 and the WT-H3R was not observed when the latter receptor was activated with the endogenous agonist histamine. For all graphs data are means ± SEM from 3 replicates from representative experiments. Where SEM bars are not visible, they are smaller than the symbol size. The quantitative analysis is shown in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 2.