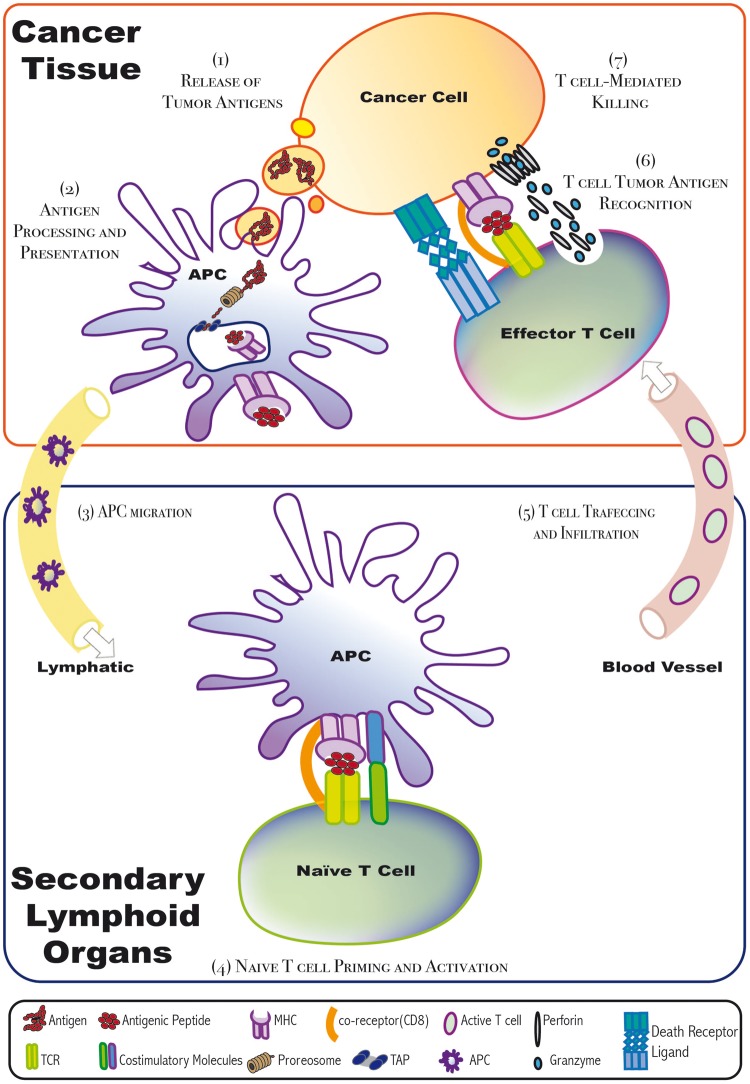
Figure 2:
Cancer–immunity cycle. When tumor-infiltrating APCs recognize tumor antigens, they get activated and thus migrate to secondary lymphoid organs. There, the APC interacts and promotes the priming and activation of antigen-specific-naïve T cells. Then, these active T cells, when infiltrated to the tumors through blood vessels, can recognize tumor antigens and thus kill the antigen-expressing cancer cells. Cytotoxic T cells kill their targets via either the death receptor pathway or the granule exocytosis pathway. ER = endoplasmic reticulum; APC = antigen presenting cell; MHC = major histocompatibility complex molecule; TCR = T cell receptor; TAP = transporter associated with antigen processing.