Figure 6.
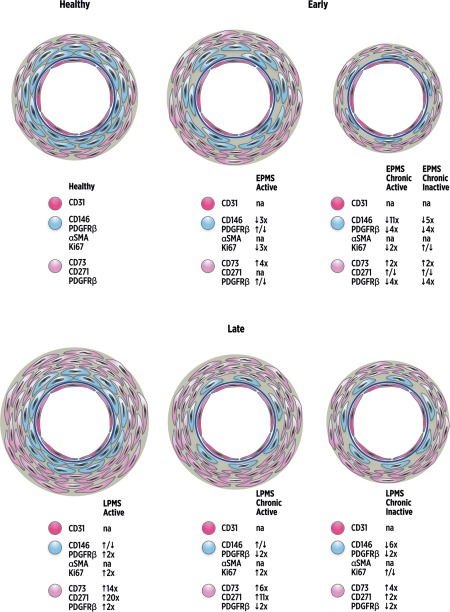
Schematic illustration of the dynamic changes in mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC)/pericyte marker localization with lesion type and multiple sclerosis (MS) disease duration. Schematic representation of vascular and perivascular dynamic changes observed following immunolocalization of MSC/pericyte markers and cell proliferation by Ki67 in MS lesion brain tissues compared to healthy controls. The images also reflect the relative changes in the quantification of immunolocalization compared to healthy tissue, demonstrated by arrows and numbers for each marker (i.e., ↑5x = fivefold increase). CD146+PDGFRβ+α‐SMA+Ki67+ staining displayed a subendothelial localization (blue cells), separated from the CD31+ endothelial cell layer (dark pink cells) and basement membrane (dark blue circle), with CD73+CD271+PDGFRβ+Ki67– staining in the adventitial and perivascular area (light pink cells). Active lesions in early progressive MS (EPMS) tissues presented with decreased immunolocalization of CD146 and Ki67, a similar distribution of PDGFRβ and increased CD73 immunostaining compared to healthy control tissue. CD271 immunostaining was not quantified in EPMS active lesions. EPMS chronic active and chronic inactive lesions both exhibited loss of CD146, and loss of PDGFRβ in chronic active lesions was also seen compared to healthy tissue. CD73 and CD271 were increased in early chronic active but similar in early inactive lesions compared to healthy. However, late stage progressive MS (LPMS) active lesions presented with enlarged regions of PDGFRβ, CD73, CD271, and Ki67 compared to healthy control tissues. LPMS chronic active and chronic inactive lesions showed loss of CD146 and PDGFRβ, but CD73 and CD271 significantly increased in the adventitia and perivascular areas compared to healthy tissue. Ki67 was significantly amplified in chronic active lesions but unchanged in chronic inactive lesions of LPMS compared to healthy tissue. CD31 and α‐SMA immunostainings were not quantified (na = not applicable). Abbreviations: α‐SMA, alpha‐smooth muscle actin; PDGFRβ, platelet‐derived growth factor receptor beta.
