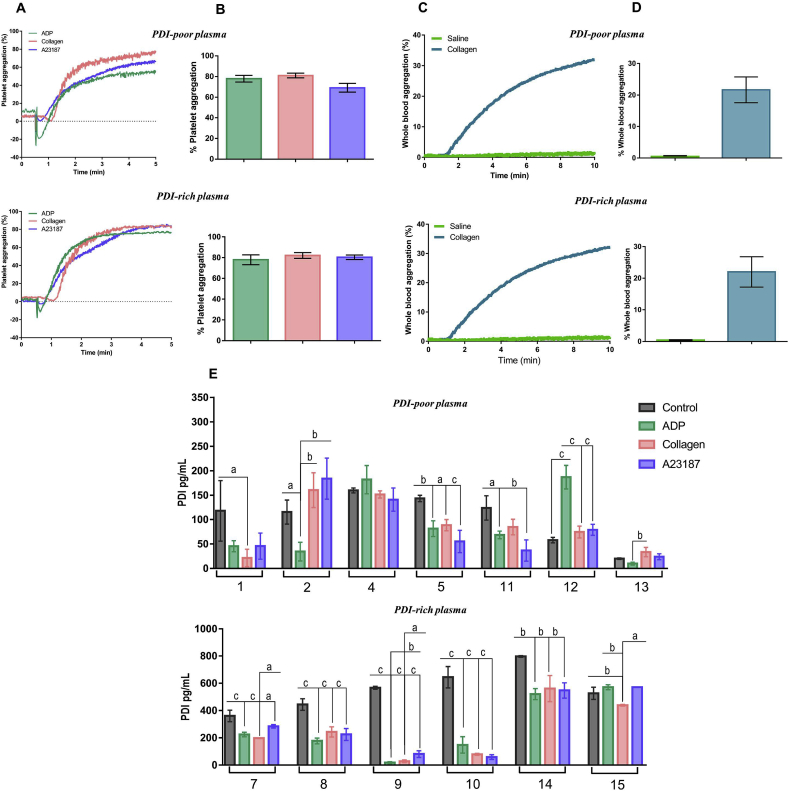
Fig. 4.
Platelet aggregation in individuals with PDI-poor or PDI-rich plasma. Experiments were performed in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) by light transmission and whole blood by impedance (in both cases 2–3x108 platelets mL−1, 37 °C). Platelets were stimulated with agonists and tracings were recorded for 5 min for PRP and 10 min for whole blood. A. Representative platelet aggregation tracings induced by 10 μM ADP, 5 μg/mL collagen and 20.5 μM A23187. B. Maximal extents of aggregation from (A). No difference was detected among groups. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post test. C. Representative whole blood aggregation tracings induced by 25 μM collagen. D. Maximal extents of aggregation from (C). No difference was detected between PDI-poor and PDI-rich plasma groups for stimulated aggregation. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post test. E. Soluble PDI was measured by ELISA in supernatants of resting (control) or activated PRP as described in Materials and methods. Numbers represent different individuals. All data represent mean ± SEM from 6 to 7 independent experiments. ap<0.05; bp < 0.005; cp < 0.0005 (One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post test, for each individual samples).