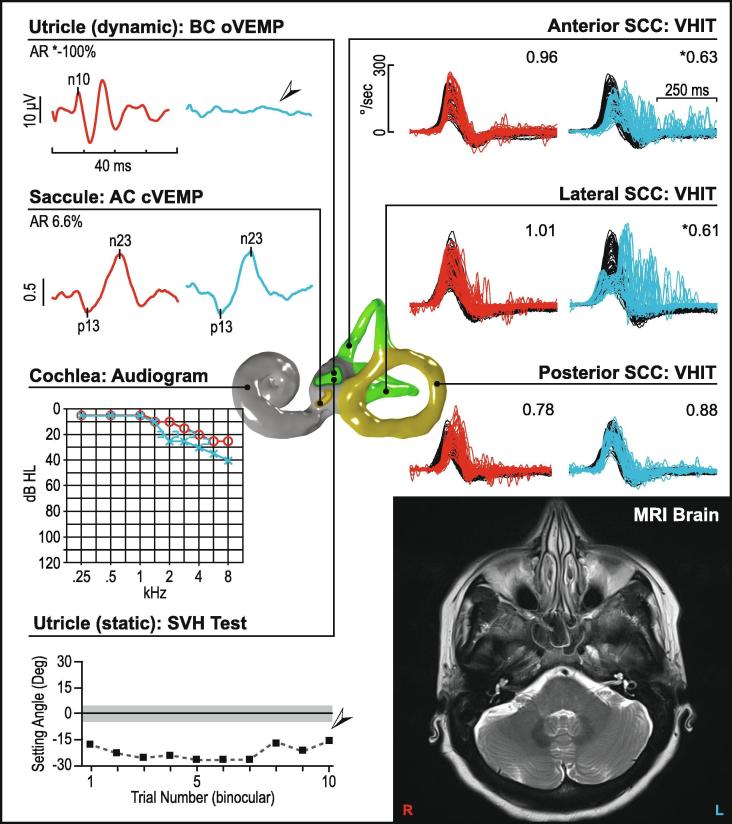
Fig. 10.
Vestibular neuritis (left ear). This figure illustrates a pattern of abnormality consistent with the superior portion of the vestibular nerve being affected in a patient with vestibular neuritis. In the affected ear oVEMPs are absent, while cVEMPs are preserved bilaterally. Video head impulses (vHITs) are reduced in the anterior and lateral semicircular canals, while posterior canals are unaffected. The audiogram shows essentially normal and symmetric hearing with a mild sloping sensorineural hearing loss, which is age-consistent. Subjective visual horizontal testing is significantly abnormal showing a leftward bias. MRI of the brain is normal. In Fig. 10, Fig. 11, Fig. 12, Fig. 13, Fig. 14, Fig. 15, Fig. 16, right ear results are in red, left ear results are in blue. vHIT gains are listed in the upper-right corner of each recording. cVEMP amplitude is shown as a corrected amplitude (ratio), after dividing the peak-to-peak value by the mean rectified EMG. Asymmetry ratios are given for VEMPs and calorics. Arrows and asterisks indicate results which fall outside the normal limits. [Abbreviations: AR; asymmetry ratio, dB HL; Decibels hearing level, Deg; Degree, kHz; Kilohertz, SCC; Semicircular canal, SVH; subjective visual horizontal, UW; unilateral weakness.]