1.
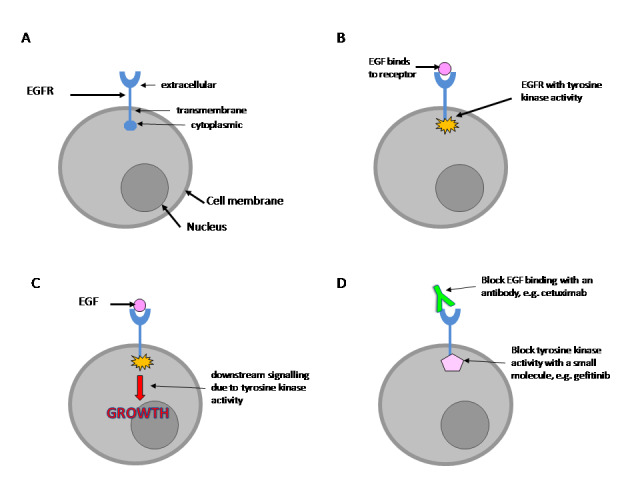
(A) The EGFR is a transmembrane protein. (B) Following binding to its ligand, EGF, the EGFR is stimulated and develops tyrosine kinase activity. (C) Tyrosine kinase activity sets off a sequence of downstream events that lead to stimulation of cell growth. (D) EGFR activity can be blocked by antibodies that prevent EGF binding to the receptor or by use of chemicals that inhibit tyrosine kinase enzyme activity.
