FIG 1.
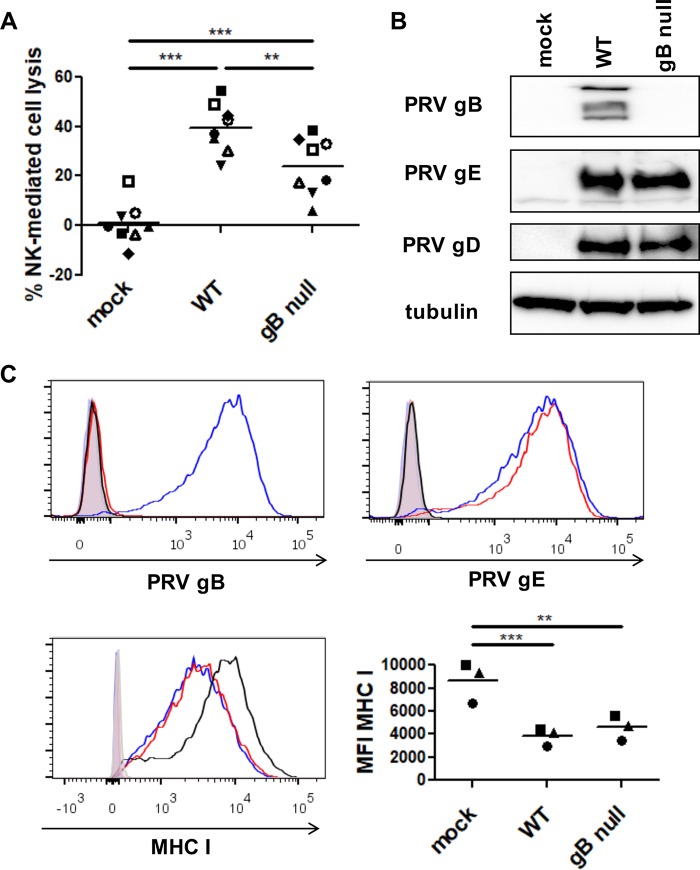
Expression of PRV gB contributes to NK cell-mediated killing of PRV-infected cells. (A) SK cells were mock infected or infected with WT PRV or isogenic gB-null PRV (MOI, 10), collected at 12 hpi, and subsequently incubated with IL-2-primed porcine primary NK cells at a target/effector cell ratio of 1:25 for 4 h at 37°C. Viability of target cells was assessed by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometric analysis, and the percent NK cell-mediated lysis was calculated. The dot plot shows the results of 8 independent repeats, and the mean value is marked by a horizontal line. Statistically significant differences are indicated with asterisks (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (B) Mock-infected SK cells and SK cells infected with WT PRV or isogenic gB-null PRV were collected at 12 hpi and subsequently analyzed by Western blotting for expression of gB, gD, gE, and tubulin. (C) SK cells were collected at 12 hpi and subsequently analyzed by flow cytometry for the expression of PRV gB (left upper panel), PRV gE (right upper panel), and MHC class I (left lower panel). An overlay of the fluorescence intensities of the different samples (open histograms) and isotype controls (shaded histogram) is shown (black, mock-infected SK cells, blue, WT PRV-infected SK cells, red, gB-null PRV-infected SK cells). The graph (right lower panel) shows the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of MHC class I expression on infected SK cells. The data shown in the graph were calculated based on the MFI minus that of the isotype control-labeled cells. The dot plot shows the results of three independent repeats, and the mean value is marked by a horizontal line. Statistically significant differences are indicated with asterisks (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).