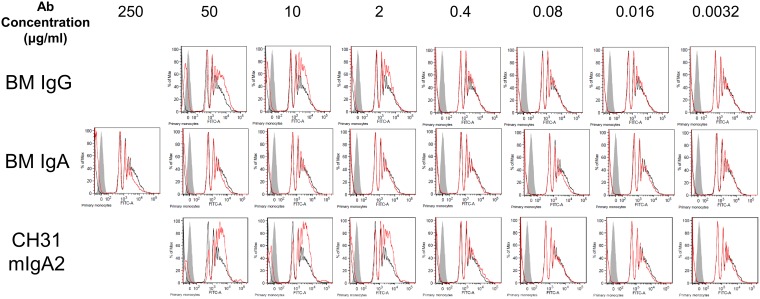
FIG 8.
Lack of detectable milk IgA-mediated phagocytosis despite increasing IgA concentration. To determine if lack of milk IgA phagocytosis activity was due to lower HIV-1 specific activity in IgA than that in IgG, higher concentrations of IgA and IgG were purified from the milk of an HIV-positive lactating woman recruited in the United states. Breast milk (BM) IgG, breast milk IgA, and a control antibody, CH31 mIgA2, were tested for phagocytosis of HIV ConS gp140-coated beads at 5-fold dilutions as indicated, and flow cytometry diagrams indicative of the phagocytosis results are shown. The red traces indicate sample antibody setup while black traces indicate the no-antibody control setup, and gray fill indicates the no-target control setup. Antibody-mediated phagocytosis is indicated by a greater area under the curve for the red trace than that for the black trace. Milk IgG and CH31 mIgA2 showed antibody-mediated phagocytosis activity down to 2 μg/ml, while milk IgA showed no antibody-mediated phagocytosis activity even at 250 μg/ml.