FIG 7.
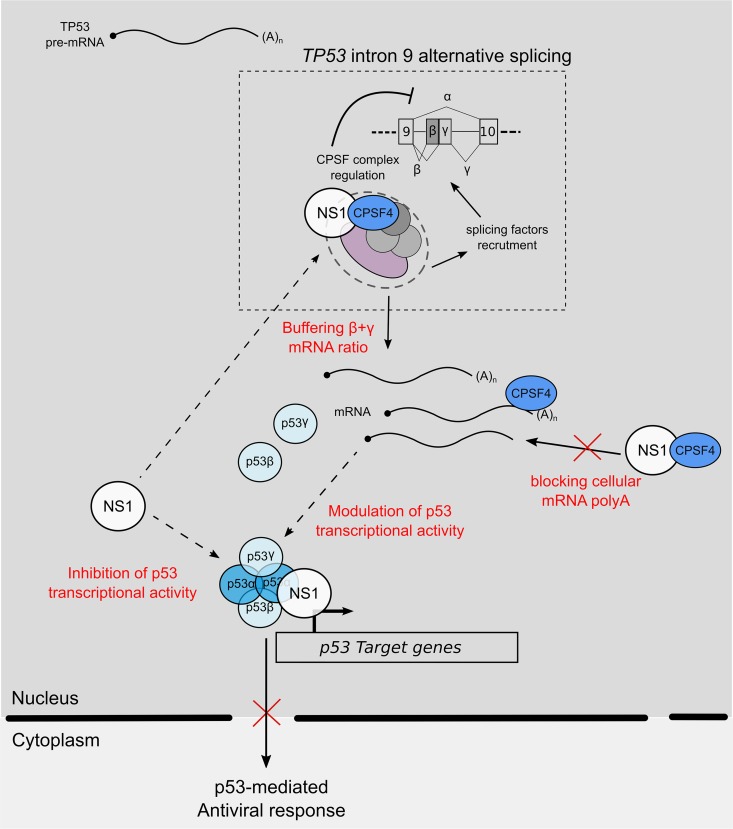
Working model of interplay between IAV NS1 protein, cellular factor CPSF4, and TP53 splicing. During IAV infection, IAV NS1 inhibits p53 transcriptional activity via its interaction with p53 but also via the modulation of TP53 splicing by “buffering” the function of CPSF4 in mRNA maturation and splicing. As a result, the spliced p53 isoform modulation of p53 transcriptional activity, and notably p53-mediated antiviral responses, coupled to the cellular impact of CPSF4 blockade positively influences viral production. When NS1 is mutated, preventing its binding to CPSF4, this regulation loop is impaired, and the antiviral response is increased, limiting viral production.