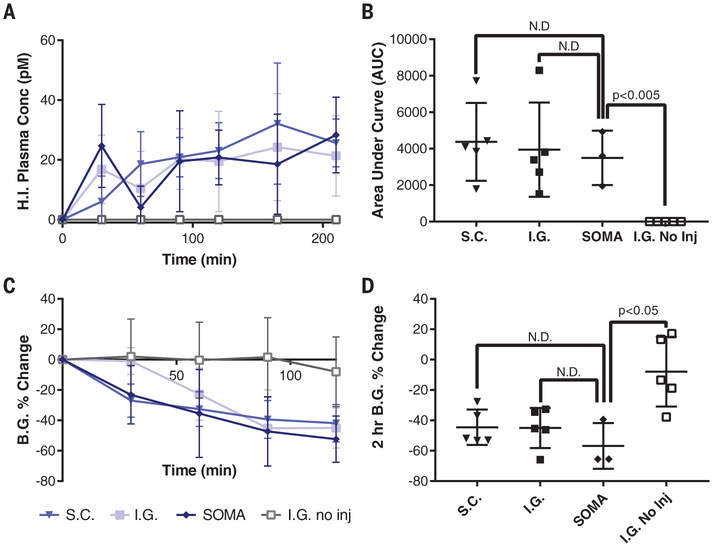
Fig. 4. In vivo API millipost delivery and device evaluation.
(A and B) Blood plasma levels for human insulin (H.I.) recorded in swine after manual subcutaneous millipost injection (S.C.) (n = 5), intragastric (I.G.) surgical millipost placement (n = 5), or I.G. millipost placement via a SOMA (n = 3). These swine are compared with animals dosed with SOMAs designed to localize the millipost to the tissue wall without injection (I.G. no inj.) (n = 5). 300 μg of human insulin was submerged underneath the tissue for each injection trial. Manually placed milliposts contain 80% human insulin and 20% PEO 200k. (C and D) All swine administered with an insulin injection demonstrated hypoglycemia, and many were rescued with dextrose. The SOMA datasets only include swine with successful fasting without residual food or measurable gastric fluid.
Error bars indicate SD. N.D., no statistically significant difference.