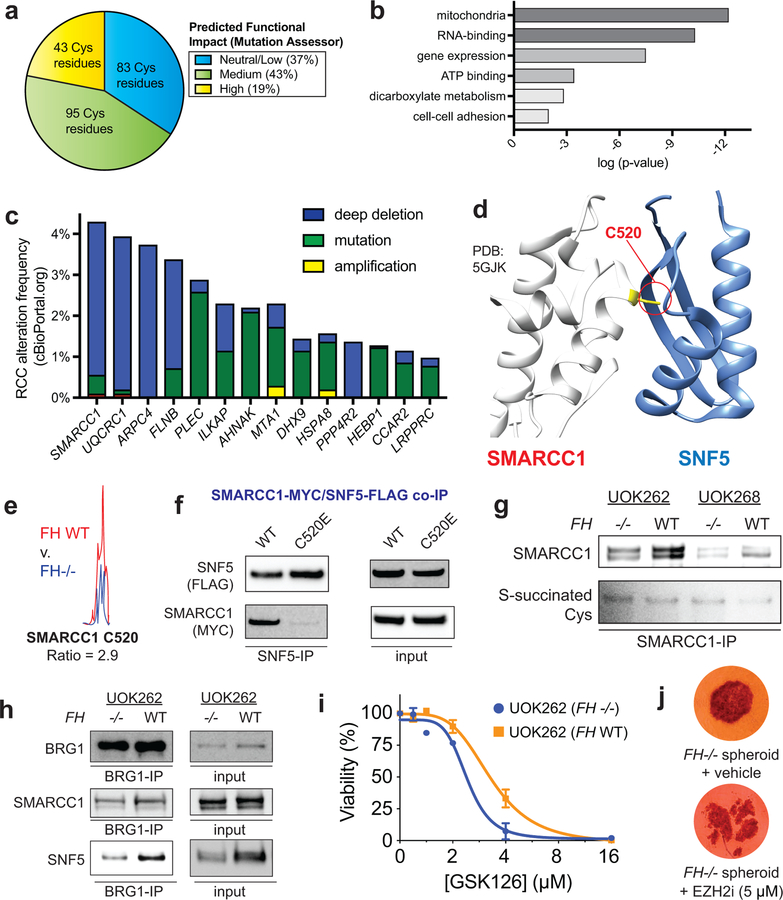
Figure 5.
Functional analyses of FH-regulated Cys residues. (a) Percentage of FH-regulated Cys residues predicted to be functional using the informatics tool Mutation Assessor (R ≥1.5, n ≥2). (b) Gene ontology analysis of FH-regulated Cys residues. (c) Correlation between genes containing FH-regulated Cys residues and genetic alterations in kidney cancer (RCC). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test (two-tailed, unpaired); **P < 0.01. (d) SMARCC1 C520 lies in the SWIRM domain and is highly conserved. (e) SMARCC1 C520 lies at the SNF5 subunit interface. (f) SMARCC1 C520 undergoes FH-regulated changes in occupancy in HLRCC cells (n = 3 independent experiments). (g) SMARCC1 C520E mutation limits co-immunoprecipitation with SNF5 in HEK-293 cells co-overexpressing FLAG-tagged SNF5 with Myc-tagged SMARCC1. (h) SMARCC1 S-succination can be detected in FH-deficient and FH WT HLRCC cell lines after IP of endogenous SMARCC1. (i) SNF5 demonstrates decreased co-immunoprecipitation and decreased levels in FH−/− HLRCC cells. Left: Results from SWI/SNF complex co-immunoprecipitation with BRG1 antibody. Right: Endogenous levels of SWI/SNF complex members in HLRCC cells. Representative images from two independent experiments are shown in g-i. Uncropped scans of immunoblots are provided in Supplementary Fig. 10. (j) EZH2 inhibitors exhibit modest selectivity for FH-deficient HLRCC cells. UOK262 FH −/− or FH WT spheroids were treated with GSK126 (21 days; 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 μM) and % viability plotted relative to the vehicle treated spheroids. Data is presented as mean ± s.d.; n = 3/group. (k) EZH2 inhibitors are toxic to HLRCC spheroids. UOK262 FH −/− spheroids were treated with vehicle or EPZ6438 (14 days; 5 μM). Figure is representative of 6 replicates.