Figure 8. Plasmin activates cell-signaling in BMDMs.
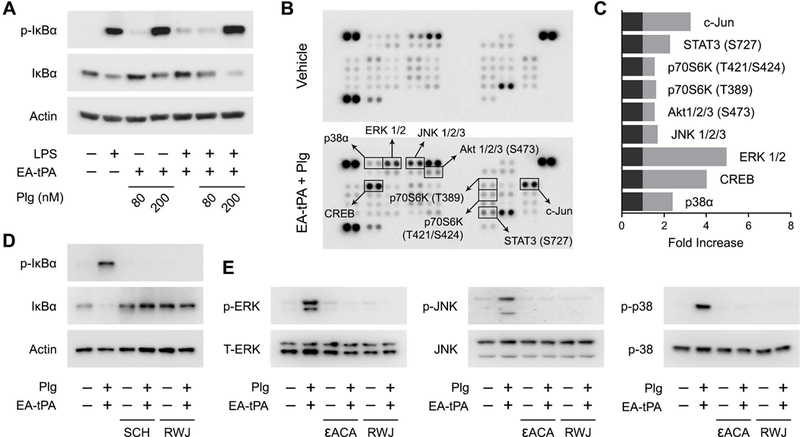
(A) BMDMs were treated for 1 h with LPS (0.1 μg/mL) or vehicle in the presence or absence of 12 nM enzymatically-active tPA (EA-tPA) and increasing concentrations of plasminogen (Plg). Equal amounts of cellular protein (20 μg) were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect phospho-IκBα, total IκBα and β-actin. (B) BMDMs were treated with EA-tPA (12 nM) plus Plg (200 nM) or vehicle for 1 h. Protein phosphorylation was analyzed by array. Changes in phospho-epitopes, associated with the tPA/plasminogen treatment protocol, exceeding 1.6× are shown in boxes. (C) Densitometry analysis of the array shown in Panel B. The fold-increase in each phospho-epitope is shown. (D) BMDMs were pre-treated with RWJ-56110 (RWJ) (30 μM) for 2 h and then with EA-tPA (12 nM) plus Plg (200 nM) or with vehicle for 1 h. Separate cells were treated with EA-tPA plus plasminogen or with vehicle for 1 h in the presence and absence of SCH-79797 (SCH) (2 μM). Cell extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect phospho-IκBα, total IκBα, and β-actin. (E) BMDMs were treated with EA-tPA (12 nM) plus Plg (200 nM), εACA (10 mM), EA-tPA plus Plg and εACA, SCH (2 μM), EA-tPA plus Plg and SCH, or vehicle for 1 h. Cell extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect phospho-ERK1/2, total ERK1/2, phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK), total c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), phospho-p38 MAP kinase, and total p38 MAP kinase.
