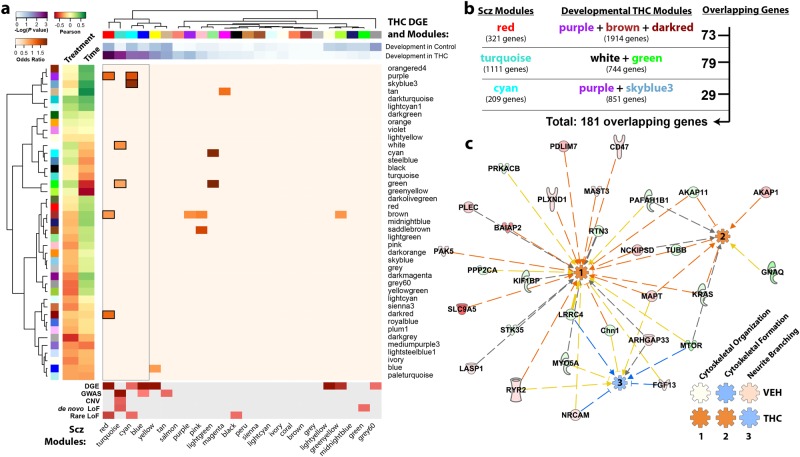
Fig. 5.
Genes developmentally dysregulated by adolescent exposure to THC are also dysregulated in the DLPFC of humans with schizophrenia. a Enrichment analysis shows significant overlap between genes differentially expressed by developmental THC and co-expression modules identified in human schizophrenia. In addition, these schizophrenia CommonMind Consortium (CMC) modules overlapped with developmental THC co-expression modules further suggesting a common epigenetic landscape. b Pathway analysis was performed on an overlapping set of 181 genes to further explore the biological relevance of these shared genes. c Ingenuity pathway analysis revealed that these genes are predicted to enhance cytoskeletal function (organization and formation) and suppress neurite branching in the THC-treated animals, but not in the vehicle-treated animals (see Supplementary Fig. 7), based on differential expression