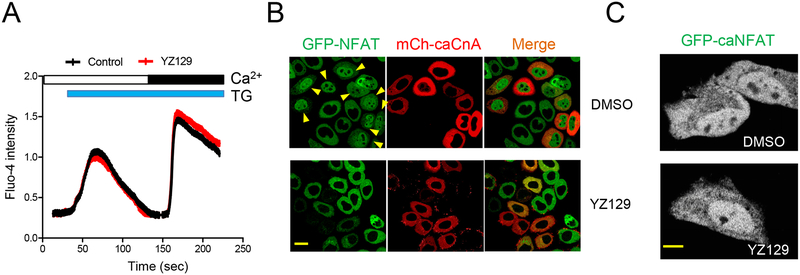
Figure 4. YZ129 inhibits the calcineurin-NFAT pathway independent of Ca2+ influx A.
The effect of 5 μM YZ129 on store depletion-induced Ca2+ influx. Empty bar, 0 mM Ca2+ in the external medium; Black bar, 1 mM Ca2+. Blue bar, 1 μM TG used to passively induce store depletion.
B. The effect of YZ129 on NFAT nuclear translocation (green) induced by a constitutively active calcineurin (caCnA; red). mCherry (mCh)-tagged caCnA was transfected into an NFAT1-GFP stable HeLa cell line to induce nuclear entry of NFAT1-GFP (arrow). Transfected cells were either treated with DMSO or YZ129 (50 μM). Note that caCnA-induced NFAT nuclear entry was inhibited by YZ129. Scale bar, 20 μm.
C. YZ129 failed to suppress the nuclear localization of a constitutively active NFAT1 (caNFAT1). GFP-tagged caNFAT1 was transfected into HeLa cells, treated with DMSO (control) or YZ129 (50 μM). Scale bar, 10 μm.