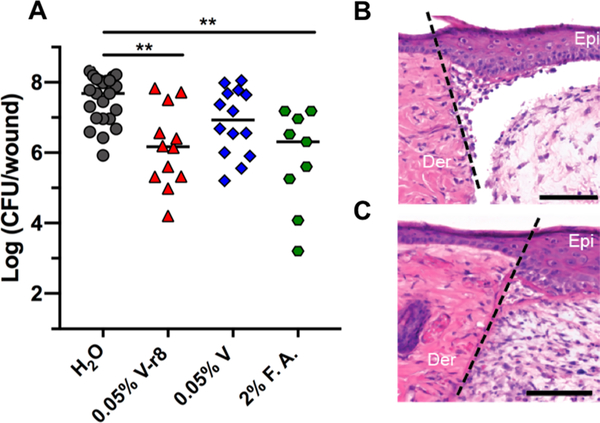
Figure 4.
In vivo evaluation of V–r8 in a skin wound biofilm model. (A) Each data point represents Log(CFU/wound) from one mouse, with the median values indicated by bars. Data were compiled from two to three independent experiments containing four to five animals per treatment group. Statistical analysis was performed using the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post ad hoc test for intergroup comparisons. **P < 0.01. To examine in vivo cytotoxicity, sterile wounds were generated and inoculated with water (B) or 0.05% V–r8 (C) in the absence of bacteria. The epidermis and dermis layers from mice treated with V–r8 appeared similar to those from mice treated with water and showed no signs of necrosis or apoptosis by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Wound healing was comparable between groups indicated by dermal granulation tissue formation and epidermal healing. A small increase in neutrophil infiltration was observed in V–r8-treated mice as compared to untreated mice. Dotted line represents the site of wounding. Epi: skin epidermis; Der: skin dermis. Scale bars = 100 μm. Images are representative of three independent samples.