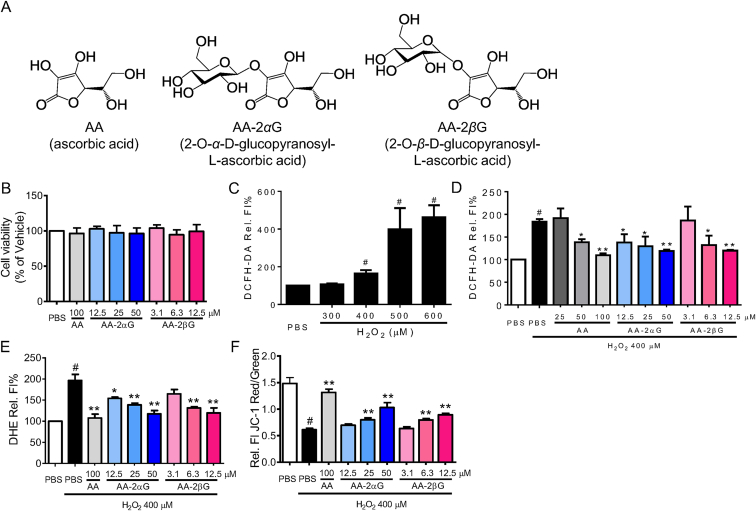
Fig. 1.
Treatment with AA, AA-2αG, and AA-2βG prevented H2O2-induced cell death in RAW264.7 cell. (A) Chemical structures of AA, AA-2αG, and AA-2βG. (B) RAW264.7 cell viability was measured by MTT assay after treatment with different AA, AA-2αG, and AA-2βG concentrations for 4 h. (C) RAW264.7 cells were treated with different H2O2 dosages of for 30 min. The H2O2-stimulated ROS generation was measured by DCFH-DA staining. RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with different f AA, AA-2αG, and AA-2βG concentrations for 1 h, followed by H2O2 treatment for another 30 min. Generation of ROS was analyzed by (D) DCFH-DA and (E) DHE staining, and (F) the effect on mitochondrial transmembrane potential was measured using JC-1 staining. The results are presented as mean ± SD from three separate experiments (*, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 compared with H2O2 treatment; #, p < 0.05 compared with PBS treatment).