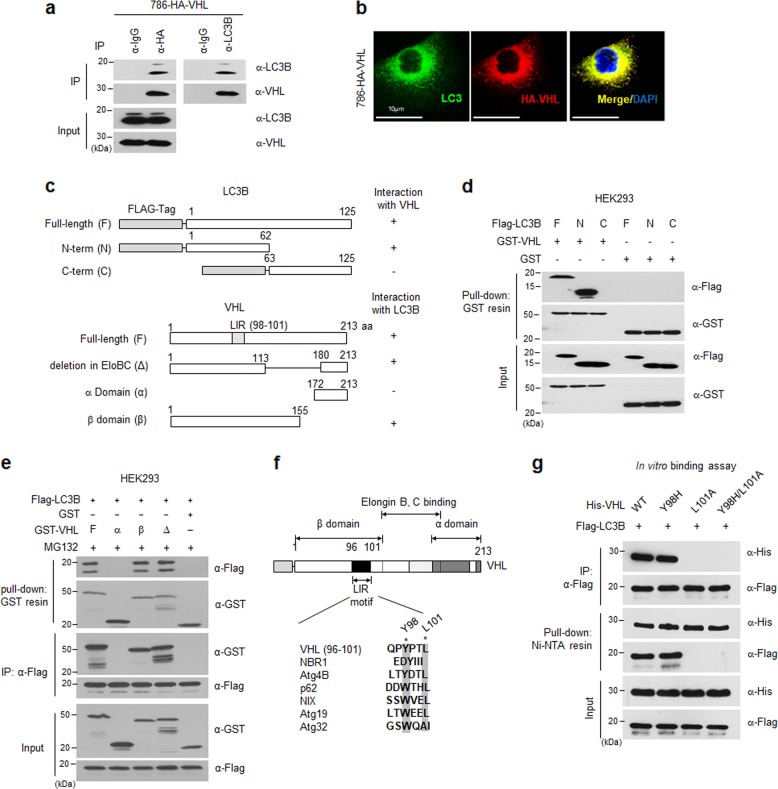
Fig. 3. Identification of the LIR motif of VHL required for interaction with the N-terminus of LC3B.
a Interaction of endogenous VHL and LC3B was assessed using immunoprecipitation assay and analyzed using western blotting with the indicated antibodies. b For detecting co-localization of endogenous VHL and LC3B, cells were stained with anti-LC3B (FITC-conjugated anti rabbit-IgG, green) and anti-VHL (rhodamine-conjugated anti mouse-IgG, red), and observed using confocal microscopy. c Schematic of different LC3B (top) and VHL (bottom) mutants. d HEK293 cells were transfected with 5 µg each of wild-type Flag-LC3B (F; 1–125 amino acids) or its various mutants (N; 1−62 amino acids or C; 63−125 amino acids) and 5 µg of GST-VHL or GST plasmids. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were pulled down with GST-Sepharose resin and analyzed using western blotting. e HEK293 cells were transfected with 5 µg each of wild-type GST-VHL (F; 1−213 amino acids) or its various mutants (α; 172−213 amino acids, α-domain; β; 1−155 amino acids, β-domain; Δ; 114−179 amino acid deletion, deletion of elongin B/c bind site) and 5 µg GST-VHL or GST plasmids for 24 h. Next, the cells were harvested, pulled down with GST resin, and analyzed using western blotting. f Schematic of the LIR motif of VHL and its various mutants. g Wild-type His-VHL or fusion proteins of its various mutants were expressed and purified from Escherichia coli. Flag-tagged LC3B was purified using anti-Flag agarose bead in Flag-LC3B overexpressing HEK293 cells. Each indicated protein (1 µg) was incubated at 4 °C overnight, immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody or pulled down with Ni-NTA resin and analyzed using western blotting with the indicated antibodies