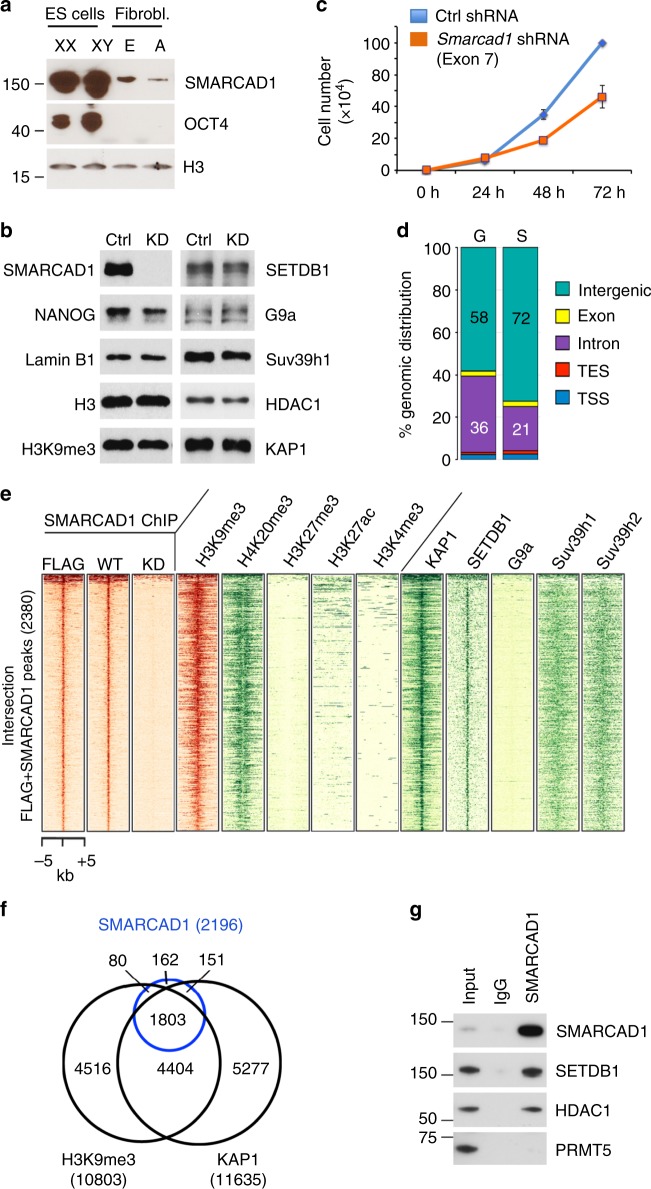
Fig. 1.
SMARCAD1 associates with heterochromatin in mESCs. a Western blot showing SMARCAD1 levels in pluripotent mouse cells (XX PGK12.1 and XY E14 ESCs), embryonic (E) and adult (A) fibroblasts. OCT4 confirms the pluripotent state, histone H3 serves as a loading control. b Knockdown of SMARCAD1 in mESCs. Western blot was performed on control (Ctrl) and Smarcad1 knockdown (KD) PGK12.1 cell extracts using antibodies specific for indicated proteins and modifications. Lamin B1 served as a loading control. MW markers are shown in Supplementary Figure 11. c Reduced proliferation of stable SMARCAD1 knockdown ESCs. Growth curves of PGK12.1 cells represent the mean ± SD from technical triplicates. Additional proliferation assays are shown in Supplementary Figure 1b. d Genomic distribution of SMARCAD1 binding sites (S) in comparison to the complete mouse genome (G). Data represent the intersection of the FLAG and SMARCAD1 ChIP (2380 regions) in PGK12.1 ESCs. TSS and TES correspond to transcriptional start site (−300 bp) and end sites (±500 bp). SMARCAD1 binds predominantly at intergenic sites (72%), with 2.4% exon, 21% intron, 1.6% TES, and 2.7% TSS. e Heatmap showing SMARCAD1 binding regions (±5 kb) corresponding to the intersection of the FLAG and SMARCAD1 ChIP-seq (2380 regions) in PGK12.1 ESCs. All regions were centered to the summit of the SMARCAD1-WT peaks and were sorted in descending order of signal intensity. Left, FLAG ChIP-seq and SMARCAD1 ChIP-seq data from WT and knockdown (KD) cells. Center and right panels show ChIP-seq intensity levels for histone marks and indicated chromatin proteins respectively, revealing SMARCAD1 co-localization with ERV-specific heterochromatic features. ChIP-seq profiles produced in this study are displayed in red, published datasets in green. f The vast majority (82%) of SMARCAD1 peaks are shared between KAP1 and H3K9me3. Venn diagram comparing the SMARCAD1 binding sites (Interesection of FLAG and SMARCAD1; 2196 peaks) with the H3K9me3 profile (10,803 peaks; this study) and KAP1 binding sites (11,635 peaks34). g SMARCAD1 is associated with SETDB1 and HDAC1 in ESCs. A SMARCAD1-specific antibody co-immunoprecipitates SETDB1 and HDAC1 from mESC nuclear extracts in the presence of benzonase and ethidium bromide, which prevents DNA mediated interactions. PRMT5 is a negative control. Lane 1, 3% input; lane 2, IgG; lane 3, IP