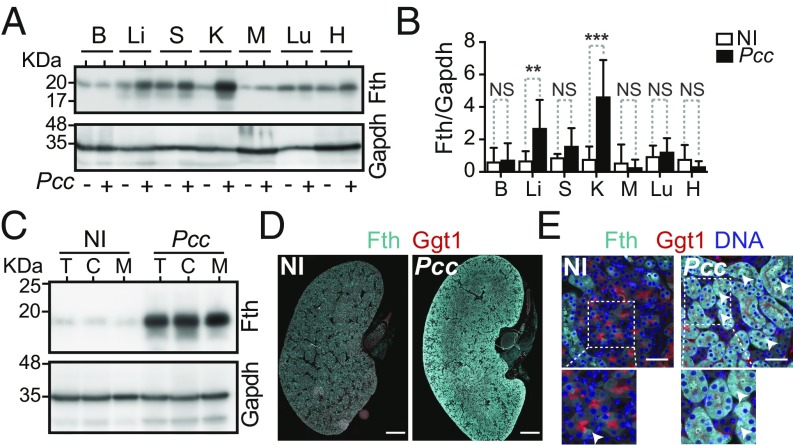
Fig. 3.
FTH expression is induced in RPTEC during Plasmodium infection. (A) Fth and Gapdh protein expression in brain (B), liver (Li), spleen (S), kidney (K), muscle (M), lung (Lu), and heart (H) of C57BL/6 mice, noninfected (NI) or 7 d after Pcc infection. Western blot representative of nine mice, from two independent experiments with the same trend. (B) Densitometry analysis (mean ± SD) of proteins shown in A. n = 9 mice per group from two experiments. (C) Fth and Gapdh protein levels in total kidney (T), renal cortex (C), and renal medulla (M) of C57BL/6 mice, not infected (NI) or 7 d after Pcc infection. Data are representative of four mice per group from one experiment. (D) Kidney immunostaining in C57BL/6 mice, noninfected (NI) or 7 d after Pcc infection. Gamma glutamyl transferase 1 (Ggt1; red) was used as a RPTEC marker. Image is representative of three mice per group in one experiment. (Scale bar: 1,000 µm.) (E) Kidney immunostaining, as in D. DAPI (blue) was used to counterstain DNA. Arrowheads highlight Fth (cyan) in Ggt1+ RPTEC. Images are representative of five random fields from four to six mice per group in one experiment. (Scale bar: 50 µm.) P values in B determined using Mann–Whitney U test. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.