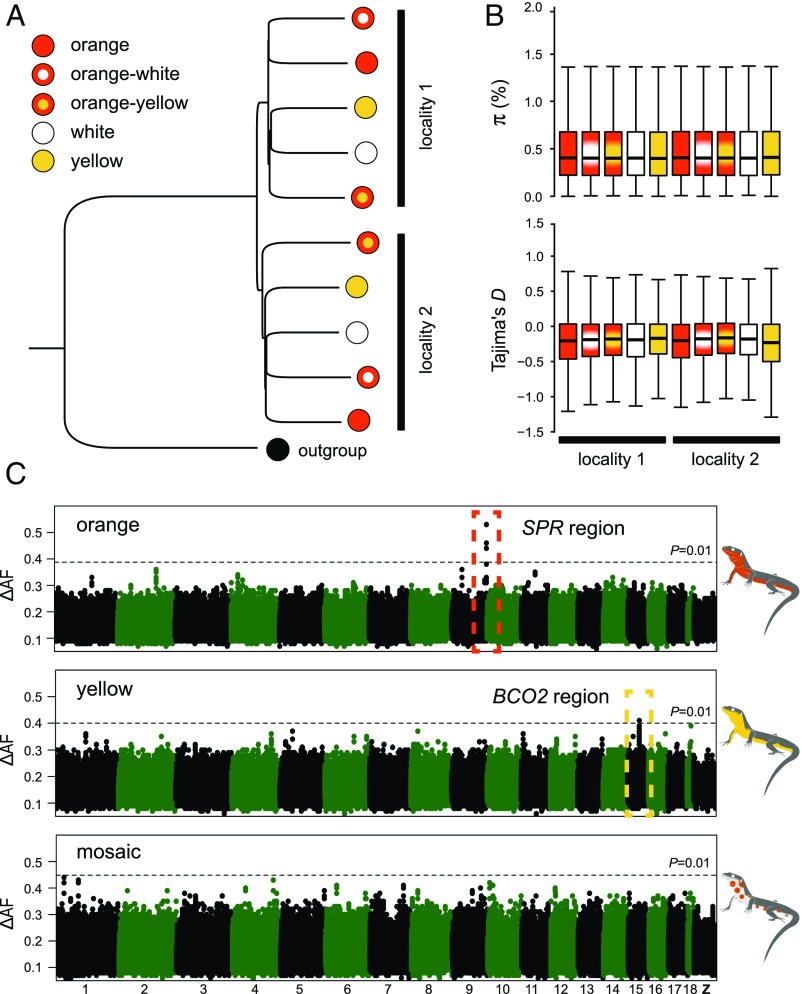
Fig. 2.
Population structure and genetic basis of color polymorphism in the common wall lizard. (A) Neighbor-joining tree summarizing genetic distance among individual pools using 250,000 randomly chosen SNPs. The tree was rooted with a DNA pool of individuals sampled from Italy and belonging to a different intraspecific sublineage. (B) Nucleotide diversity (π) and Tajima’s D estimated for each morph. Both statistics were calculated in 10-kb nonoverlapping windows, and a genome-wide estimate was obtained by averaging all windows across the genome. (C) Genetic mapping based on differences in allele frequencies (ΔAF) for the orange, yellow, and mosaic phenotypes. The Manhattan plots show the median value of 20-SNP windows (five-SNP overlap) across the reference genome. The dashed lines represent a 1% significance cutoff based on 1,000 permutations conducted for each dataset.