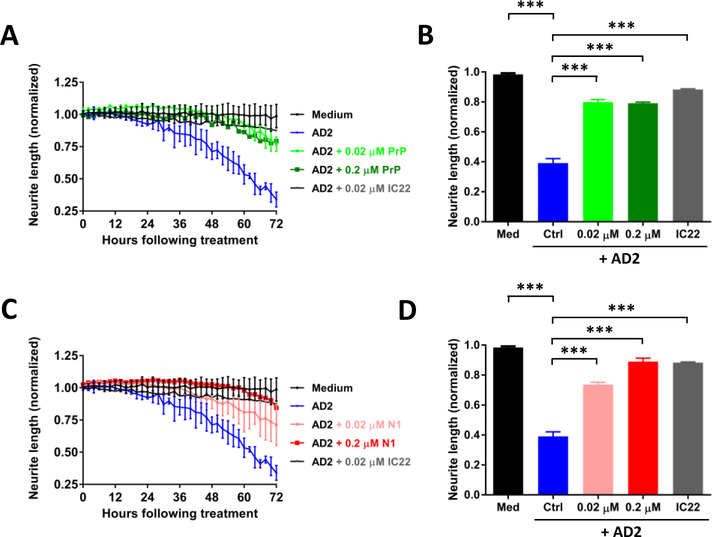
Figure 5. PrP and N1 protect against Aβ-induced neuritotoxicity.
The same paradigm as in Figure 4 was employed to monitor the effects of the Aβ-containing AD 2 brain extract on iNs and whether or not PrP and N1 protein could protect neurons. On post-induction date 21, iNs were treated with medium alone (black circles), AD 2 extract (blue), or AD 2 extract plus 0.02 μM PrP (light green), 0.2 μM PrP (dark green), or IC22 (gray). (A) Time-course plot shows that AD2 extract caused neuritotoxicity and this could be attenuated by treatment with either PrP or IC22. Each data point is the average of 3 wells ± SD. (C) Similar results could be obtained by treatment with N1 protein. Coincubation of iNs with AD 2 extract plus 0.02 μM N1 protein (light red) and 0.2 μM N1 protein (dark red) reduced AD brain extract induced neuritotoxicity. (B and D) Neuritic length was averaged over the last 6 h of imaging, and values normalized to pre-treatment measurements. Differences in means were assessed with ANOVA followed by Bonferoni`s post-hoc test. The results shown are from a single experiment. *** p<0.001.