Figure 3. Specific mutation category identified by whole exome sequencing in 114 families with chronic kidney disease.
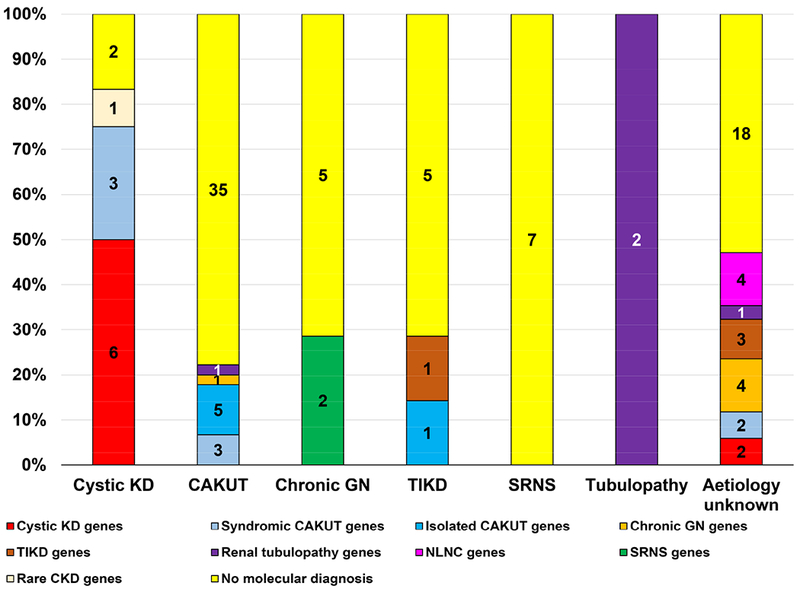
The X-axis displays the 7 a priori clinical diagnostic groups listed horizontally and includes cystic kidney disease (KD), congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT), chronic glomerulonephritis (GN), tubulo-interstitial kidney disease (TIKD), steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS), renal tubulopathy (tubulopathy) and CKD - aetiology unknown. The Y-axis displays the molecular genetic diagnosis established following whole exome sequencing and includes the following:
i) Mutations in known cystic kidney disease including nephronophthisis genes (red) identified
ii) Mutations in known syndromic CAKUT genes (light blue) identified
iii) Mutations in known isolated CAKUT genes (dark blue) identified
iv) Mutations in known chronic glomerulonephritis (GN) genes (orange) identified
v) Mutations in known tubulo-interstitial kidney disease (TIKD) genes (brown) identified
vi) Mutations in known renal tubulopathy genes (purple) identified
vii) Mutations in known steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) genes (green) identified
viii) Mutations in known nephrolithiasis/nephrocalcinosis (NLNC) genes (pink) identified
ix) Mutations in known rare chronic kidney disease genes (miscellaneous category) (cream) identified
x) No molecular genetic diagnosis established following WES (yellow)
