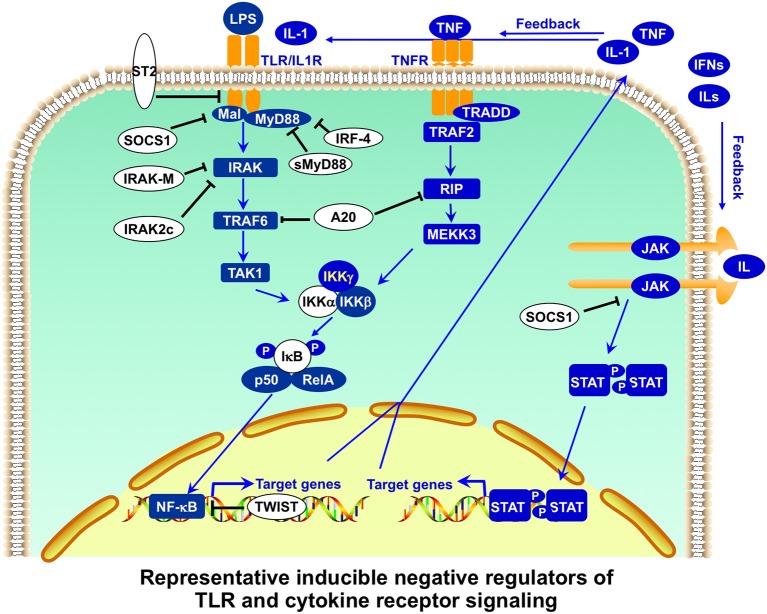
Figure 4.
Representative inducible negative regulators of TLR and cytokine receptor signaling in APCs. Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is further regulated by inducible negative regulators in a feedback manner. Membrane-bound ST2 interacts with MyD88 and Mal, and sequesters MyD88-dependent nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) from activation. MyD88s (the short form of MyD88) antagonizes MyD88 functions. Intracellular IRAKM (interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase M) inhibits the dissociation of IRAK-IRAK4 and subsequent formation of IRAK-TRAF6. SOCS1 promotes the ubiquitination of Mal for degradation. A20 has dual functions of ubiquitination and deubiquitination of RIP and TRAF6 (tumor-necrosis factor-receptor-associated factor 6) for their degradation, inhibiting both TLR and TNFR signaling. Transcription repressor Twist-2 inhibits the transcription of NF-κB-targeted genes. Cytokine receptor signaling is also regulated by inducible negative regulators. SOCS1, in addition to regulating TLR signaling, inhibits JAK activity as a pseudosubstrate or promotes the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of JAK. Many of these negative regulators also play important roles in regulating T-cell activation and function (65).