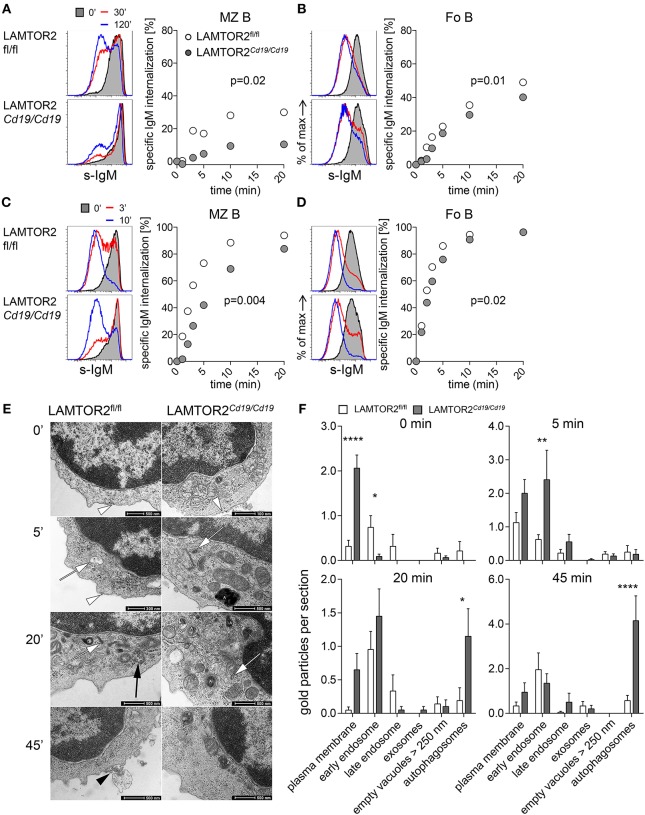
Figure 6.
Altered internalization and degradation of BCR in LAMTOR2-deficient B cells. FACS analysis of BCR internalization in splenic B cells. Passive BCR internalization in (A) MZ B, (B) Fo B cells or ligand-induced BCR internalization in (C) MZ B or (D) Fo B cells. Purified splenic B cells were labeled in an ice-cold environment with either monovalent (A,B) or bivalent (C,D) biotin-labeled anti-IgM Fab or F(ab′)2 fragments, respectively, and then BCR internalization was assessed over time at 37°C. Plots for electronically gated cells are representative for two independent experiments. Charts summarize the first 20 min of one representative experiment out of two. (E) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis of ligand-induced BCR internalization and degradation in B cells of LAMTOR2fl/fl or LAMTOR2Cd19/Cd19 mice. Purified B cells were stimulated with colloidal-gold labeled anti-IgM F(ab′)2 and analyzed at indicated time points. White arrowheads demonstrate gold particles at the cell membrane, white arrows mark early endosomes with gold-marked IgM receptors, the black arrow shows the late endosome with gold at the internal vesicles, the black arrowhead marks exosomes with attached gold particles. Autophagosomes are labeled with an “A.” (F) Quantification of TEM data. The quantitative evaluation has been done only at cells cut through the cell center to get access directly to all cell organelles. Nineteen to thirty-eight sections per time point and genotype were analyzed. Statistical significance was assessed with 2-way ANOVA (effect for genotype is shown) and Sidak's multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.001).