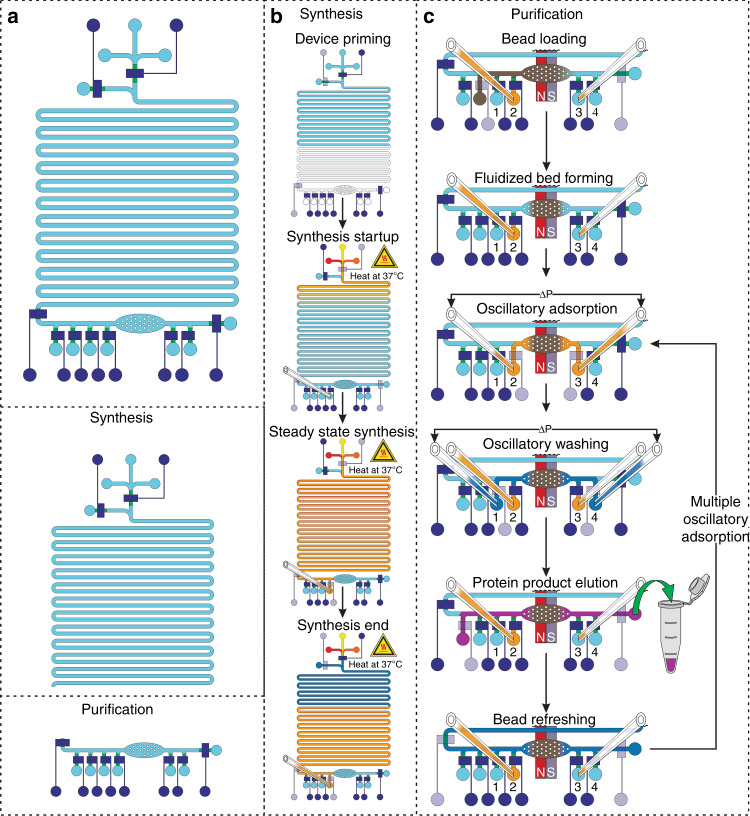
Fig. 5. Overview and operation of the integrated cell-free protein synthesis and purification platform in 5 major steps: priming, protein synthesis, protein adsorption, washing, and elution, with an optional 6th step of bead refreshing.
Dark blue denotes a closed valve, where transparency denotes an open valve. a Overview of integrated synthesis platform with identification of the synthesis and purification modules. b Synthesis operational workflow. Priming: Water is flowed into the system to prime the channel. Synthesis: The CFPS reagents are flowed into the individual inlets while being mixed and heated in the 13.2 μl reaction channel. The CFPS reaction mixture continuously flows into the attached tubings for storage. Once the desired amount of the CFPS reagents has been flowed into the system, purification buffer is flowed to force the remaining CFPS reaction mixture into tubing reservoir 2. c Purification operational workflow. Protein adsorption: After beads are flowed into the purification chamber and magnetically immobilized, the CFPS reaction mixture is loaded and the synthesized protein is adsorbed onto the beads during oscillatory adsorption. Washing: The protein-bead complexes are washed using oscillatory washing. Elution: The sythesized protein is eluted off of the bead surface. Bead refreshing: The beads are optionally refreshed for adsorption by flowing loading buffer through the bed of beads. Then the purification steps can be repeated, if desired