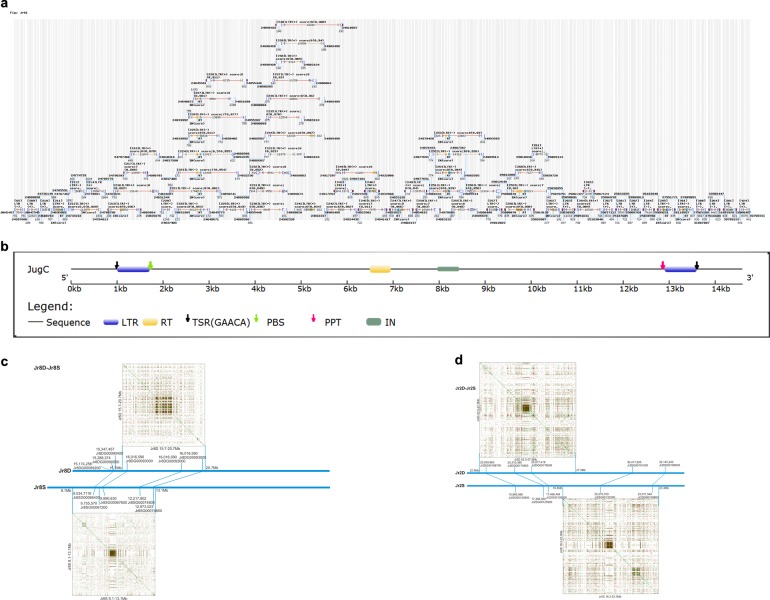
Fig. 5. Centromere structure and evolution.
a Distribution of the JCR repeats in the centromeric region of Jr2D. b Structure of the centromeric JCR Gypsy element. c and d Structural comparisons of 5-Mb intervals including the JCR arrays between J. regia homoeologous chromosome pairs Jr8D-Jr8S and Jr2D-Jr2S. Lines connect collinear loci in homoeologous chromosomes. The coordinates of the edges of the 5-Mb intervals in Mb are shown. c The Jr8D-Jr8S homoeologous chromosome pair illustrating the conservation of the centromere location on homoeologous chromosomes. A JCR array is located in the interval Jr8DG00090000-Jr8DG00105900 on Jr8D. This interval corresponds to interval Jr8SG00067200-Jr8SG00077500 on Jr8S, which also contains a JCR array. d The Jr2D-Jr2S homoeologous chromosome pair illustrating the repositioning of the JCR array into different interval without perturbation of the order of collinear genes. In Jr2D, the JCR array is within interval Jr2DG00174800-Jr2DG00176500. This interval corresponds to interval Jr2SG00125900-Jr2SG00126200 in Jr2S, which is devoid of a JCR array. Instead, a JCR array is in interval Jr2SG00133300-Jr2SG00138800 in pseudomolecule Jr2S