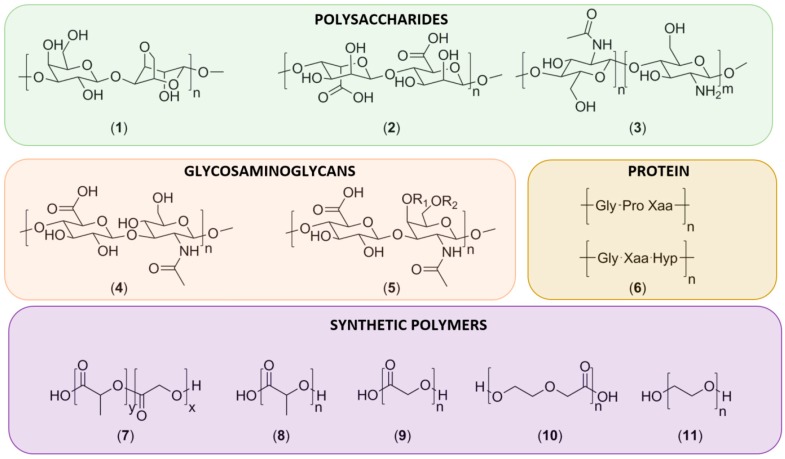
Figure 3.
Structures of commonly used (bio)polymers in cartilage repair. Displayed are the natural polymers (1) agarose, (2) alginate, (3) chitosan with partial deacetylation, (4) hyaluronic acid, (5) chondroitin-4-sulfate, where R1 = SO3H; R2 = H or chondroitin-6-sulfate, where R1 = H; R2 = SO3H, (6) collagen, showing two common tripeptide repeats, where Hyp represents L-4-hydroxyproline and X represents any amino acid other than Gly, Pro or Hyp, and is often a basic or acidic amino acid. Synthetic polymers (7) poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), (8) poly(lactic acid), (9) poly(glycolic acid), (10) polydioxanone and (11) poly(ethylene glycol).