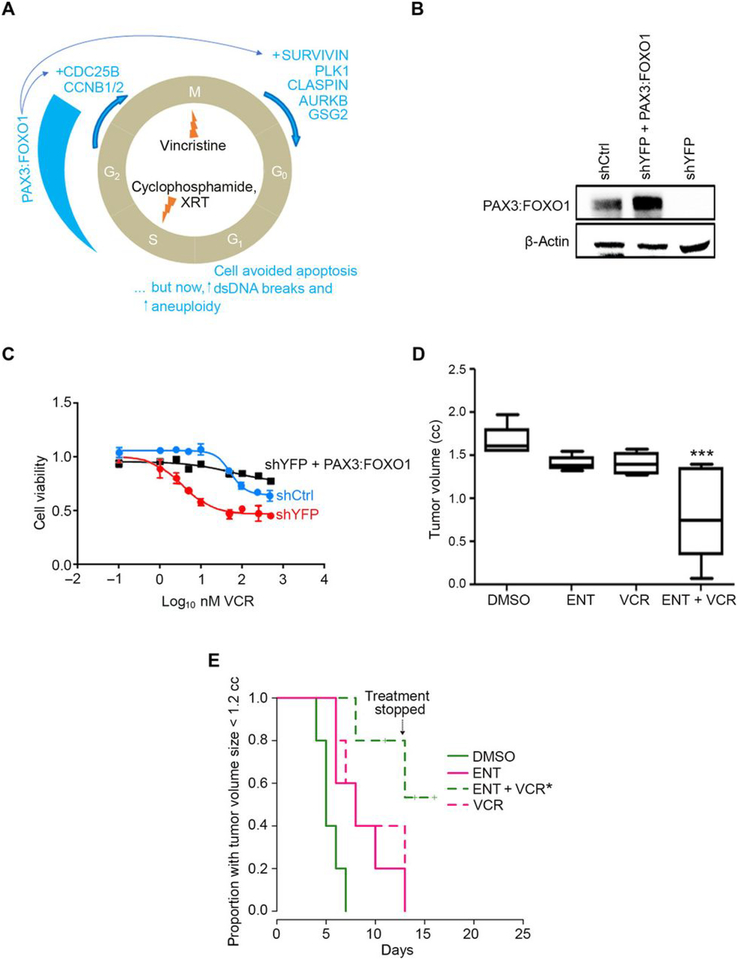
Fig. 1. Entinostat treatment of aRMS in vivo.
(A) Diagrammatic representation of checkpoint adaptation, a process whereby tumor cells survive chemotherapy and radiation in late phases of the cell cycle. XRT, X-ray telescope radiotherapy; PLK1, polo-like kinase 1; AURKB, aurora kinase B; GSG2, genomic structure of haspin; CDC25B, cell division cycle 25b; CCNB1/2, cyclin B1/2; DS, double-stranded. (B) Basal PAX3:FOXO1 protein expression in murine U23674 aRMS cells transfected with control shRNA (shCtrl), PAX3:FOXO1-targeted shRNA (shYFP), or targeted shRNA plus a lentivirus expressing PAX3:FOXO1 (shYFP + PAX3:FOXO1). Blot is representative of N=3 biological replicates. (C) Viability of the U23674 cells described in (B) exposed to vincristine (VCR) at 4 nM for 24 hours. Graph plotted using GraphPad Prism. Data are mean ± S.D. of N= 3 independent experiments. (D) Box-and-whisker plot showing the tumoristatic efficacy of entinostat (ENT) or vincristine (VCR), alone and in combination, in aRMS mice at day 13 (DMSO vs ENT+VCR). Treatment at a daily dose of 5 mg/kg of ENT by intraperitoneal (IP) injection, VCR at a dose of 1 mg/kg weekly by IP injection, or a combination of both. Data are means ± SEM (N=5 mice per cohort), ***P < 0.001 by log-rank test. (E) Kaplan-Meier plot of the proportion of mice with tumors smaller than 1.2 cubic cm after treatment with ENT and/or VCRat a daily dose of 5 mg/kg of ENT by intraperitoneal (IP) injection, VCR at a dose of 1 mg/kg weekly by IP injection, or a combination of both. Treatment was stopped after day 13 because body weight loss approached 10–15%. Data are means ± SEM (N=5 mice per cohort), *P < 0.05 by log-rank test. In this experiment, treatment was stopped for all mice after day 13 because body weight loss approached 10–15%.