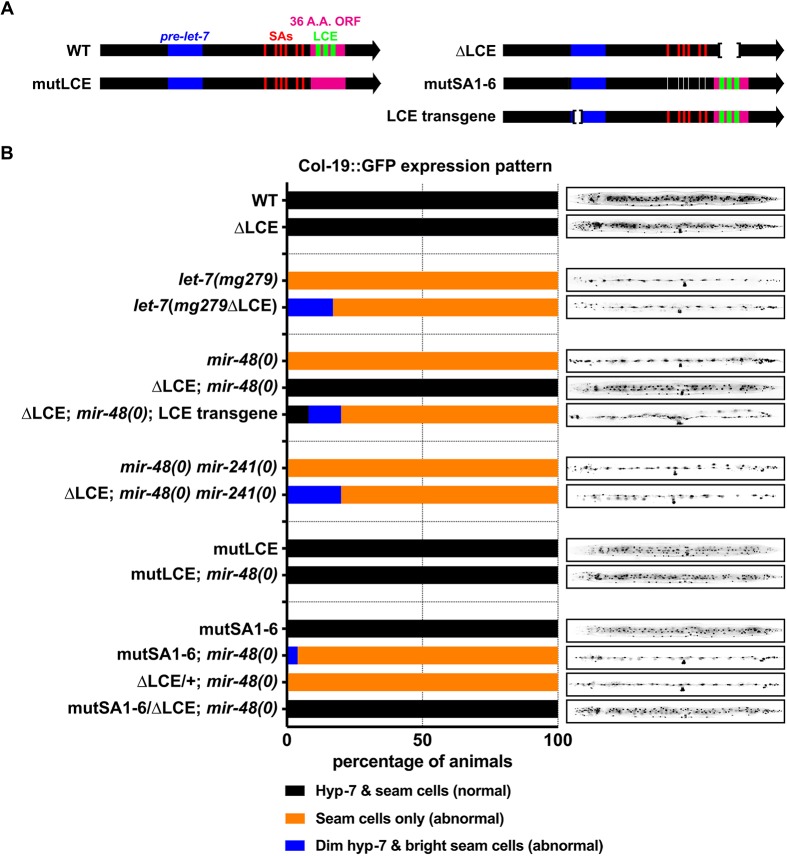
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of SL1-LCE function, either by deletion of the LCE, or by mutations of LCE-proximal trans-splicing acceptor sequences, suppresses the retarded hypodermal phenotypes of mir-48(0) animals. (A) Positions of the let-7 LCE mutations (green), SA mutants (red) and LCE transgene used in these experiments. (B) Quantification of the Col-19::GFP phenotypes observed for each genotype in molting late L4 animals (left). From top to bottom: n=9 (WT), 10 (ΔLCE), 23 [let-7(mg279)], 12 [let-7(mg279 ΔLCE)], 9 [mir-48(0)], 22 [ΔLCE; mir-48(0)], 26 [ΔLCE; mir-48(0); LCE transgene], 18 [mir-48(0) mir-241(0)], 15 [ΔLCE; mir-48(0) mir-241(0)], 10 (mutLCE), 15 [mutLCE; mir-48(0)], 10 (mutSA1-6), 10 [mutSA1-6; mir-48(0)], 11 [ΔLCE/+; mir-48(0)] and 16 [mutSA1-6/ΔLCE; mir-48(0)] animals. Images (right) are of a representative molting L4 animal for each genotype.