Figure 1. The phospholipase A2 reaction and actions of its products.
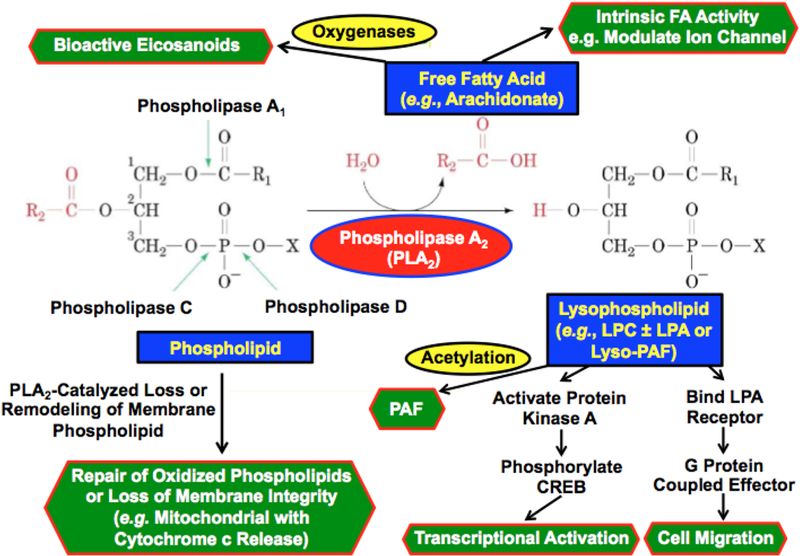
Phospholipids have a glycerol backbone and an esterified phosphate moiety at the sn-3 position that may also be esterified to a polar head group, such as choline, ethanolamine, glycerol, serine, inositol or phosphatidylglycerol. In the sn-2 position, a fatty acid moiety is esterified to the glycerol backbone. In the sn-1 position, there may be a second esterified fatty acid residue or there may be a saturated ether linkage to a fatty alcohol residue or a vinyl ether linkage to a fatty aldehdye residue. Phospholipases C cleave the diglyceride moiety from the phospho-headgroup. Phospholipases D cleave the polar head group from the phosphatidic acid moiety. Phospholipases A1 hydrolyze the sn-1 fatty acid substituent from the glycerol backbone to yield a free fatty acid and a 1-lysophospholipid, and Phospholipases A2 (PLA2) cleave the sn-2 substituent from the glycerol backbone to yield a free fatty acid and a 2-lysophospholipid. The products of PLA2 action on the phosphatidylcholine (PC) species illustrated in the figure are arachidonic acid and 2-lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Downstream effects of PLA2 action may arise from intrinsic actions of the fatty acid product or of its metabolites, such as oxygenated eicosanoids, or from actions of the lysophospholipid products or its metabolites. In the case of LPC, such metabolites could include the bioactive product lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), and an alkyl ether LPC species could also be acetylated to yield the lipid mediator Platelet Activating Factor (PAF), e.g., 1-O-hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Other downstream effects of PLA2 action can arise from remodeling or loss of the phospholipid substrate. With Group VIA PLA2 (iPLA2β) examples of downstream effects attributable to each of these possibilities are thought to occur. The free fatty acid arachidonic acid derived from iPLA2β action in pancreatic islet β-cells is thought to activate voltage-operated K+ channels83,153. A 12/15lipoxygenase product from iPLA2β-derived free arachidonic acid is thought to activate a RhoA kinase pathway to vascular smooth muscle cell activation in diabetic vasculopathy123. LPC derived from iPLA2β action is thought to participate in CREB-mediated activation of transcriptional responses to viral infection in macrophages154, and LPA derived from iPLA2β action is thought to stimulate macrophage migration into sites of vascular inflammation in diabetes111. Ether linked LPC derived from iPLA2β action appears to provide substrate for PAF biosynthesis in inflamed endothelial cells122,131,155. iPLA2β also appears to participate in the repair of oxidized cardiolipin species in mitochondria by excising oxygenated fatty acid residues, and with overwhelming mitochondrial injury this may lead to cytochrome c release and initiation of apoptosis67–69.
