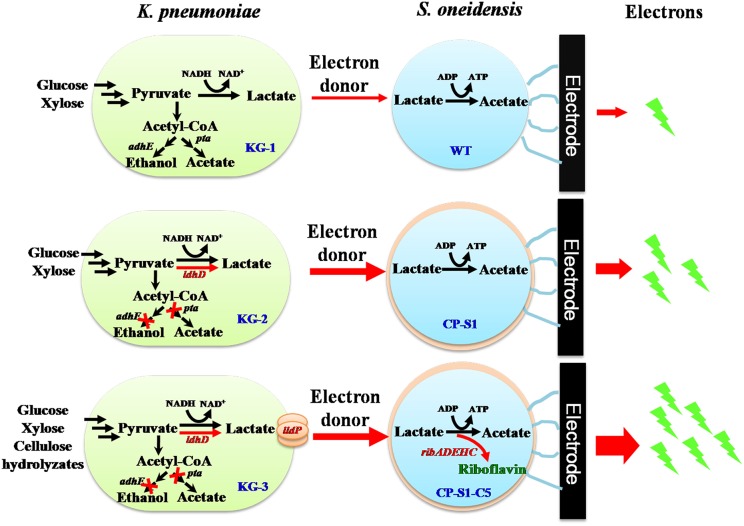
Figure 1.
Schematic of the metabolic interaction of the engineered microbial consortia with K. pneumoniae S. oneidensis in a hierarchical way. Lactate was produced by K. pneumoniae from glucose and xylose which was fed to S. oneidensis as carbon source and electron donor to generate electricity in MFCs. To direct more carbon flux to lactate biosynthesis of K. pneumoniae, we eliminated the ethanol and acetate pathway via deleting phosphotransacetylase gene (pta) and alcohol dehydrogenase gene (adhE) and further constructed a synthesis and delivery system through expressing a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhD) and a lactate transporter gene (lldP). To increase S. oneidensis adhesion to the carbon electrode to compete the surface of electrode and further facilitate flavin-mediated electron transfer, a biosynthetic flavins pathway (from Bacillus subtilis) was expressed in a highly hydrophobic S. oneidensis strain CP-S1.