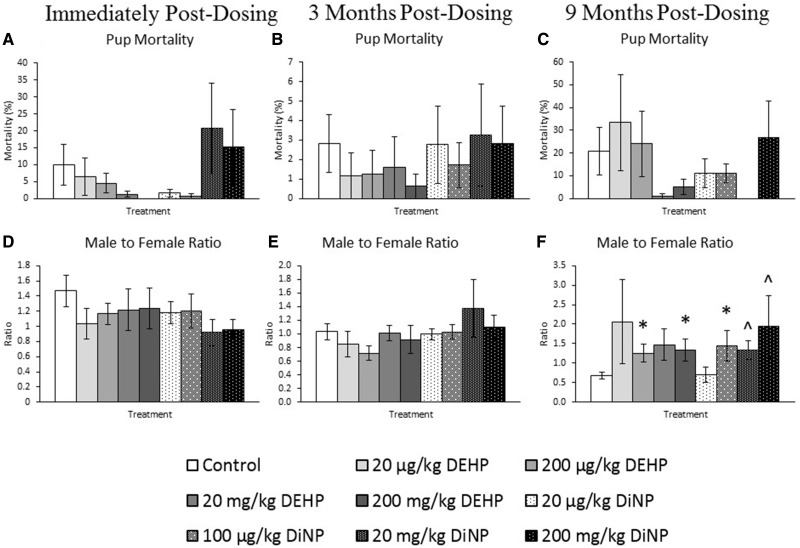
Figure 8.
Effects of DEHP and DiNP on pup mortality and sex ratio. Adult female CD-1 mice were orally dosed for 10 days with either vehicle control (corn oil), DEHP (20 µg/kg/day–200 mg/kg/day), or DiNP (20 µg/kg/day–200 mg/kg/day). Females were mated with untreated male mice for breeding trials immediately, 3, and 9 months post-dosing. Pup mortality was calculated by dividing the number of dead pups by the total number of pups within the litter and multiplying by 100 (Panels A–C, n = 9–19, 5–20, and 3–13 mice/group, respectively). The male-to-female ratio was calculated by dividing the number of male pups by the number of female pups for each litter and multiplying by 100 (Panels D–F, n = 9–18, 4–14, and n = 4–11 mice/group, respectively). Data are represented as means ± SE. Statistically significant difference when compared with control (p ≤ .05) is denoted with an asterisk (*). Borderline statistical significance (.05 < p ≤ .10) is denoted with a caret (^).