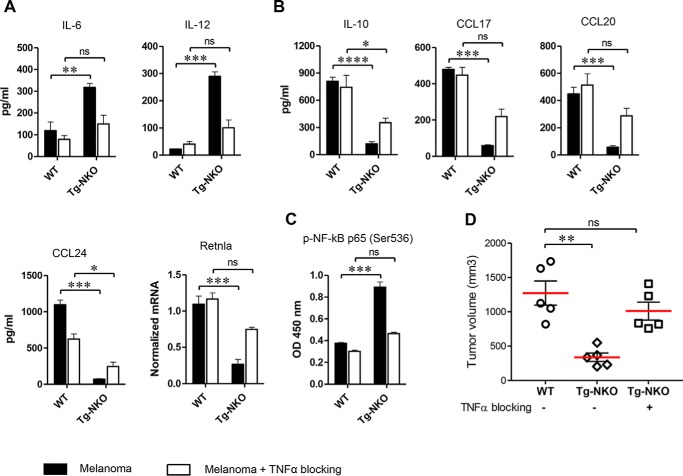
Figure 5.
Role of TNFα in enhanced M1 macrophage polarization by ACE C-domain up-regulation. Perityoneal macrophages were isolated from WT and Tg-CKO mice and conditioned 24 h with supernatant from B16-F10 melanoma (as described in Fig. 3A) in the presence of TNFα neutralizing antibody (500 ng/ml). The production of cytokines was determined in the macrophage supernatant by ELISA (n = 4/group). Cellular expression of Retnla was measured by qRT-PCR. A, pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-12. B, Anti-inflammatory markers IL-10, CC17, CCL20, CCL24, and Retnla. C, measurement of NF-κB p65 phosphorylation (Ser536) by ELISA (n = 4 for A–C). D, determination of melanoma growth with TNFα blockade. Either WT or Tg-NKO macrophages were injected intratumorally in WT mice, as described in Fig. 2E. For TNFα blockade, Tg-NKO macrophages were pretreated for 24 h with TNFα neutralizing antibody before intratumor injection, and then after injection, these mice were given the TNFα inhibitor C87 (12.5 mg/kg) by i.p. injection on days 0 and 3 (n = 5). Final tumor volume was measured 1 week after intratumor injection (day 14). One-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA were used for statistical analysis. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.005; ***, p ≤ 0.0005).