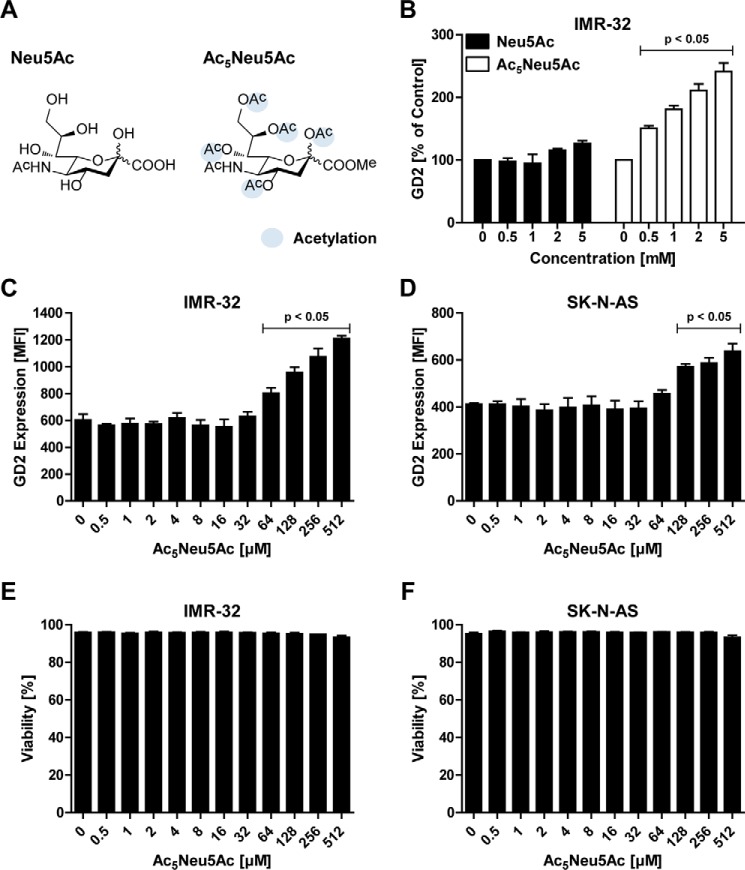
Figure 2.
Peracetylated sialic acid enhances GD2 expression. A, structural representation of Neu5Ac (left) and the peracetylated form Ac5Neu5Ac (right). B, effect of sialic acid supplementation on GD2 expression of IMR-32 cells. The cells were cultured for 3 days with 0–5 mm Neu5Ac or Ac5Neu5Ac, and GD2 expression was assessed by flow cytometry. The bar diagram shows the mean percentage of GD2 expression ± S.E. of IMR-32 cells treated with Neu5Ac or Ac5Neu5Ac normalized to control (n = 3). C and D, IMR-32 and SK-N-AS cells were cultured for 3 days with 0–512 μm Ac5Neu5Ac and stained with anti-GD2 antibody. Bar diagrams show GD2 expression of IMR-32 cells (C) and SK-N-AS cells (D) as mean fluorescence intensity ± S.E. of three independent experiments. E and F, effect of Ac5Neu5Ac on cell viability. Bar diagrams show mean percentage of viable IMR-32 cells (E) and SK-N-AS cells (F) ± S.E. in culture after treatment with 0–512 μm Ac5Neu5Ac for 3 days (n = 3).