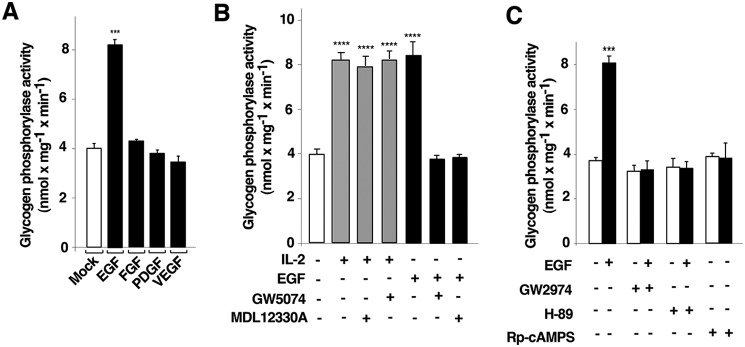
Figure 4.
Epidermal growth factor receptor activation requires RAF1 and adenylyl cyclase to induce glycogen phosphorylase activation. A, cells deprived of IL-2 for 48 h were unstimulated (−) or stimulated (+) with 10 ng ml−1 EGF, 50 μg ml−1 FGF, 20 ng ml−1 PDGF, or 10 ng ml−1 VEGF at 37 °C for 10 min and lysed. Cell lysates were used to measure glycogen phosphorylase (PYG) activity. The results presented as histograms show the mean ± S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments performed in triplicates ***, p < 0.001. B, cells deprived of IL-2 for 48 h were pretreated with an adenylyl cyclase inhibitor (10 μm MDL12330A), RAF1 inhibitor (10 μm GW5074), or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) (−) for 1 h and stimulated (+) or not (−) with 10 ng ml−1 EGF and 500 units ml−1 IL-2 for 10 min and lysed. Cell lysates were used to measure PYG activity. The results show the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. ****, p < 0.0001. C, cells deprived of IL-2 for 48 h were pretreated with 10 μm GW2974 (EGFR inhibitor), 10 μm H-89, 10 μm Rp-cAMPS (PKA inhibitors), or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) (−) and stimulated (+) or not with 10 ng ml−1 EGF at 37 °C for 10 min and lysed. Cell lysates were used to measure PYG activity. The results show the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. ***, p < 0.001.