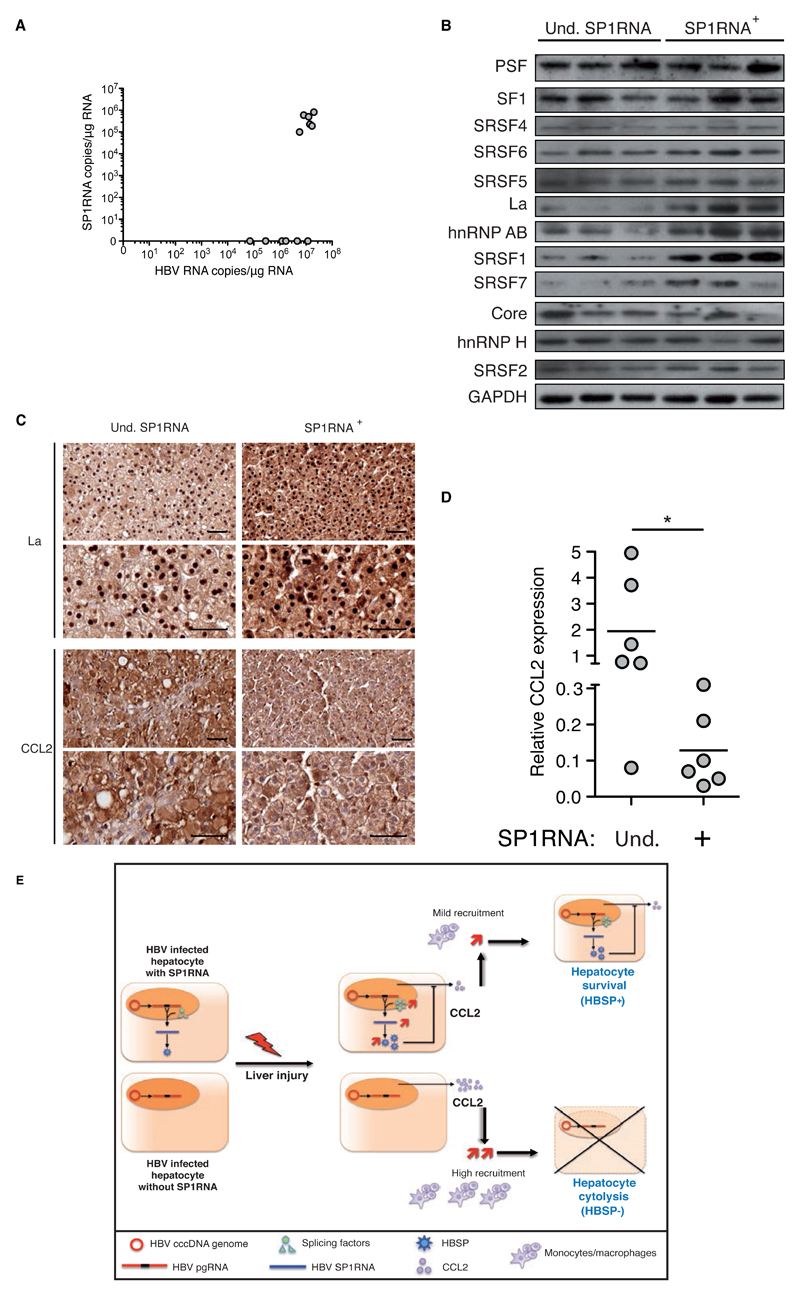
Fig.8. Association between SP1RNA, CCL2 and transregulatory splicing factors in HBV chronic carriers.
(A) HBV RNA and SP1RNA quantification in the liver of HBV chronic carriers (n=6 for undetectable (Und.) and n=6 for detectable SP1RNA groups). (B) Splicing factors expression in the liver of HBV chronic carriers with undetectable or detectable SP1RNA. (C) La and CCL2 immunochemistry on serial liver section counterstained with hematoxylin (upper and lower bar 50μm) from chronic HBV carrier with undetectable or detectable SP1RNA. (D) CCL2 mRNA quantification in the liver of HBV chronic carriers with undetectable (n=6) or detectable SP1RNA (n=6). (E) Schematic model for SP1RNA synthesis and HBSP activity during liver damage. Under liver damage SP1RNA/HBSP expressing hepatocyte through decreasing liver inflammatory microenvironment have a selective advantage leading to the increase of SP1RNA proportion during the course of HBV infection. Mann-Withney U-tests: *p<0.05 and **p<0.01.