Figure 5. Design and efficacy of TEL-2-BASP and TEL in a chemically induced CCl4 mouse model.
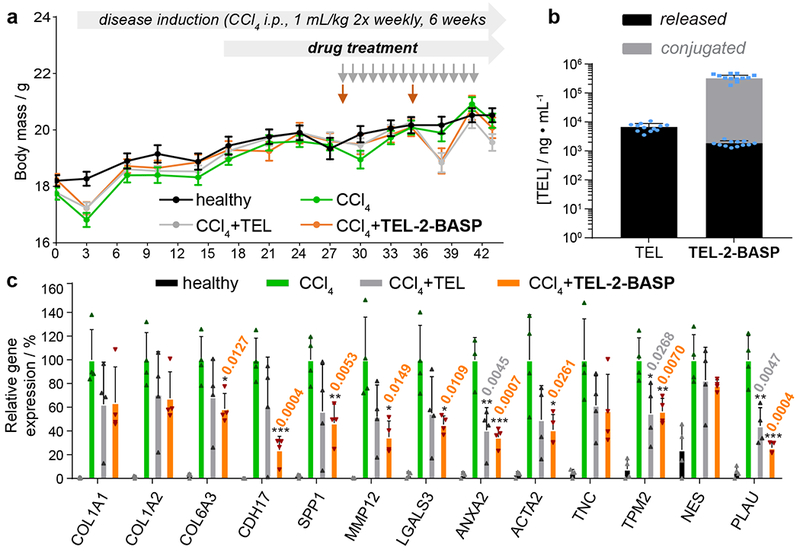
a. Experimental study design for the CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis model showing body weight measurement for all treatment groups (healthy, untreated, and test agents: TEL (10 mg/kg, p.o. q.d.; total of 14 doses) and TEL-2-BASP (700 mg/kg i.v. q.w.; total of two doses) during 6 weeks of CCl4 intoxication; data reported as mean ± SEM. b. Terminal liver PK measurements (week 6) for TEL and TEL-2-BASP (released and conjugated TEL); data reported as mean ± SEM. c. Gene expression analysis from a repeat CCl4 efficacy study comparing two doses of TEL-2-BASP (300 mg/kg i.v. q.w.) with daily administration of TEL (10 mg/kg p.o. q.d.; total of 14 doses). Relative expression levels of 13 genes that become over expressed in fibrotic tissue and are suppressed by TEL-2-BASP are shown; data reported as mean ± SD, statistical analyses performed with two-tailed Student’s t test relative to levels of CCl4 group (* = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001). Individual P values are noted above each bar when statistical differences are present.
