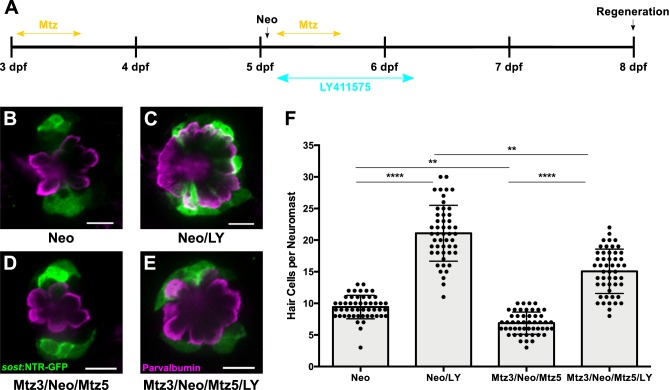
Figure 7. DV cell-ablation reduces the number of supernumerary hair cells formed during Notch-inhibited hair cell regeneration.
(A) Timeline of dual DV cell-ablation, Notch-inhibition experiment. Sost:NTR-GFP larvae were treated with Mtz at 3 dpf, treated with neomycin at 5dpf, then co-treated with Mtz and LY411575 for 8 hr, then washed out and treated with LY411575 for 16 additional hours (24 hr total LY). (B–E) Maximum projections of sost:NTR-GFP neuromasts following normal hair cell regeneration (B; Neo), Notch-inhibited hair cell regeneration (C; Neo/LY), DV cell-ablated hair cell regeneration (D; Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5), and DV cell-ablated and Notch-inhibited hair cell regeneration (E; Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5/LY). Sost:NTR-GFP cells are shown in green, and anti-Parvalbumin immunostained hair cells are shown in magenta. Scale bar = 10 μm. (F) Total number of hair cells per neuromast following hair cell regeneration. Neo: 9.42 ± 1.85, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); Neo/LY: 21.08 ± 4.42, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5: 6.86 ± 1.76, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5/LY: 15.06 ± 3.51, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); mean ± SD; Kruskal-Wallis test, Dunn’s post-test, p<0.0001 (Neo vs. Neo/LY; Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5 vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5/LY), p=0.0058 (Neo vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5), p=0.0029 (Neo/LY vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5/LY).