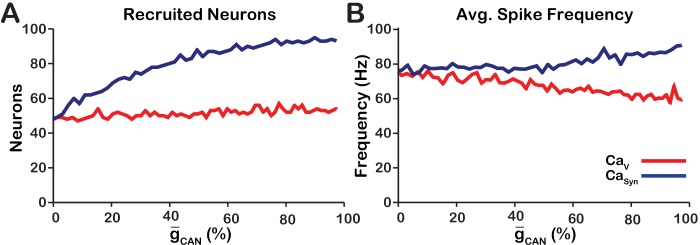
Figure 3. Calcium source and -dependent effects on cellular properties regulating network activity amplitude for the simulations presented in Figure 1.
(A) Number of recruited neurons in the modeled population of 100 neurons as a function of (%) for voltage-gated and synaptic calcium sources. The number of recruited neurons is defined as the peak number of spiking neurons per bin during a network burst. (B) Average spiking frequency of recruited neurons as a function of for the voltage-gated and synaptic calcium mechanism. Average spiking frequency is defined the number of spikes per bin divided by the number of recruited neurons. The parameters used in these simulations are: : , , and . : , , and .