Figure 1: Phylogenetic organization, domain structure, and G protein coupling of human adhesion GPCR subfamilies I-IX.
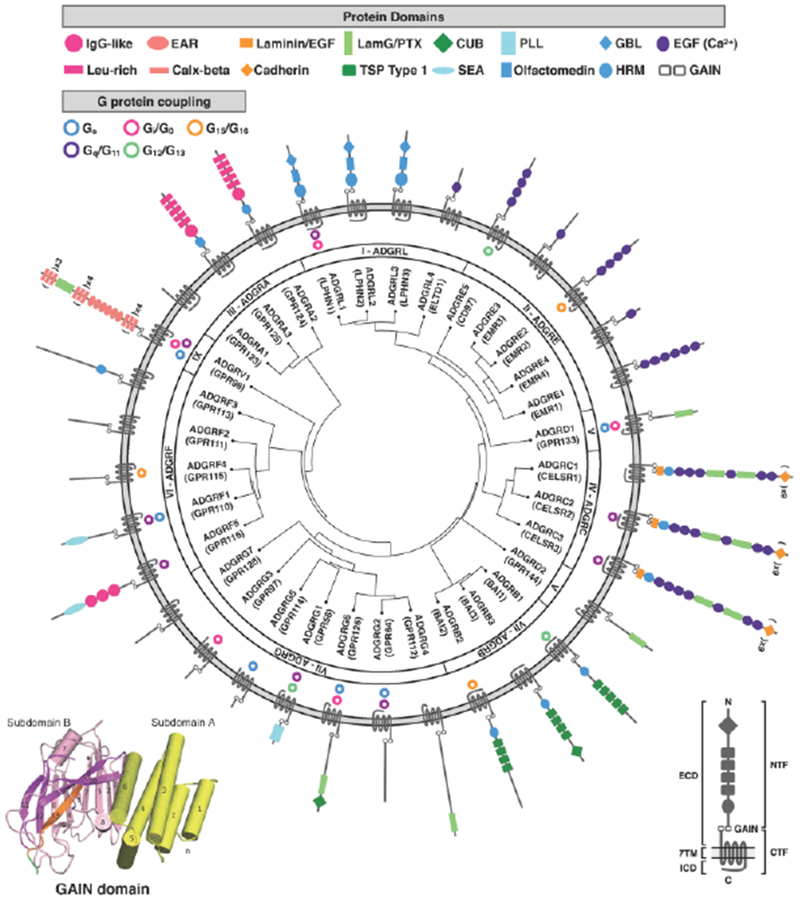
The left inset shows the GAIN domain crystal structure of rat latrophilin with subdomain A (yellow) and subdomain B (magenta), modified from [111]. The right inset identifies general domains and features of aGPCRs. All human aGPCRs are phylogenetically clustered by homology in the center ring, with gene names, aliases, and aGPCR families listed in the middle ring. G protein-coupling, when known, is illustrated in the outer ring, with the corresponding aGPCR structure and protein domains (not to scale). Receptor homology and phylogenetic clustering was performed by GPCRdb (accessed 3/19/2018). Receptor domains were determined by the NCBI Conserved Domain calculator (accessed 3/19/2018), the UniProt database (accessed 3/19/2018), and published reports. G protein coupling was determined by the Guide To Pharmacology (IUPHAR/BPS; accessed 3/19/2018) and published reports [81, 112–114]. Abbreviations used: ECD: extracellular domain; 7TM: seven transmembrane domain; ICD: intracellular domain; NTF: N-terminal fragment; GAIN: GPCR autoproteolytic-inducing domain; CTF: C-terminal domain; IgG: immunoglobulin G; Leu-rich: leucine-rich; EAR: epilepsy-associated repeat; Calx: calcium exchanger; EGF: epidermal growth factor-like domain; LamG/PTX: laminin G/pentraxin; TSP: thrombospondin repeat; CUB: complement C1r/C1s, Uegf, Bmp1; SEA: sperm protein/enterokinase/agrin; PLL: pentraxin (PTX)/laminin/neurexin/sex-hormone-binding globulin (LNS)-like; GBL: galactose-binding lectin; HRM: hormone motif; EGF (Ca2+): calcium-binding EGF domain.
