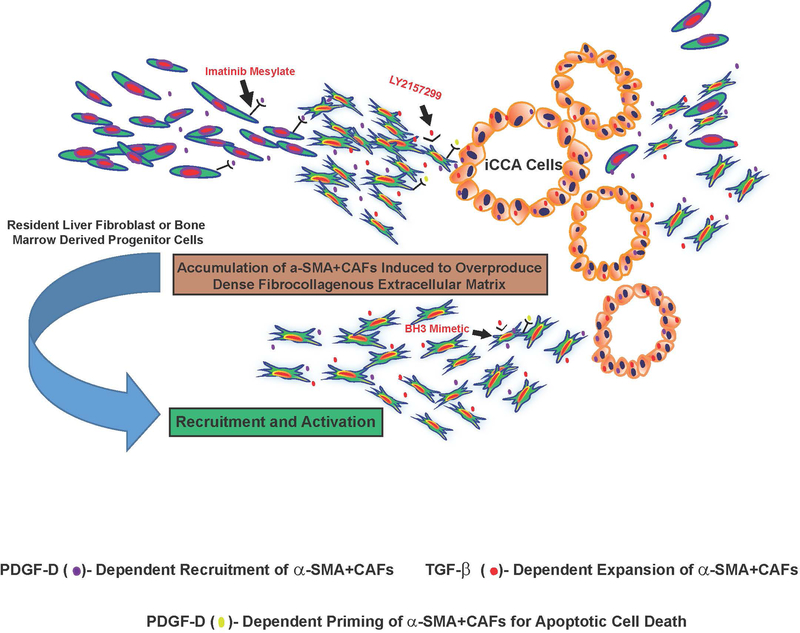
Figure 2.
Schematic representation illustrating PDGF-D and TGF-β as key drivers of the desmoplastic reaction in iCCA. Resident liver fibroblasts that include portal fibroblasts, hepatic stellate cells, and periductular fibroblasts, as well as possibly fibroblastic cells derived from bone marrow progenitor cells have been suggested as potential sources of CAFs in iCCA stroma. By interacting with its cognate receptor PDGFRβ expressed by fibroblastic cells, PDGF-D secreted by cholangiocarcinoma cells has been shown to stimulate fibroblast migration mediated by Rho GTPases, notably Rac1, Cdc42 and JNK, thereby providing a novel mechanism for CAF recruitment in cholangiocarcinoma. Selective inhibition of PDGFRβ with imatinib mesylate, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor currently in clinical use for other cancer inhibitory indications, significantly blocked fibroblast migration by cholangiocarcinoma cells in vitro. In addition, PDGF-D was demonstrated to prime CAFs for apoptosis via Puma-mediated Bak activation, which could then be converted to full-blown apoptosis by BH3 mimetics. TGF-β, which is overexpressed in iCCA, being produced by both cholangiocarcinoma cells and by stromal cells, has further been shown to be an essential mediator of the desmoplastic cholangiocarcinoma phenotype in a 3-dimensional cholangiocarcinoma cell-α-SMA+CAF co-culture model, by provoking significant increases in proliferative α-SMA+CAFs together with the formation of a dense fibrocollagenous extracellular matrix characteristic of the in situ tumor. Galunisertib (LY2157299), a clinically relevant TGF-β signaling pathway inhibitor was further determined to produce a prominent dose-dependent attenuation of the dense fibrocollagenous matrix, which was accompanied by a significant decrease in α-SMA+CAFs accumulated within the supporting matrix. These findings collectively support PDGF-D and TGF-β as being important regulators of the desmoplastic reaction in iCCA and suggest novel strategies for abrogating CAF recruitment and accumulation within iCCA that may be of potential therapeutic benefit.