Figure 8.
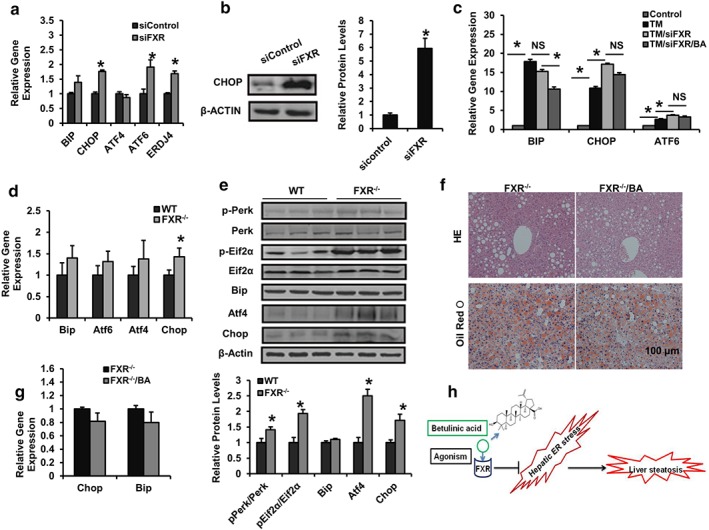
FXR mediates the ameliorative effect of BA on NAFLD and hepatic ER stress. (a, b) At 48 hr after being transfected with siRNA for control or FXR, HepG2 cells were treated with PA (500 μM) for 24 hr and analysed by RT‐PCR and immunoblotting. The relative protein levels are shown. (c) At 48 hr after being transfected with siRNA for control or FXR, HepG2 cells were treated with DMSO or betulinic acid (50 μM) in the presence or absence of TM for 24 hr and analysed by RT‐PCR (d, e) 15‐week‐old wild type female C57BL/6J mice as WT and FXR−/− mice were fed chow diet, livers were harvested and subjected to mRNA and immunoblotting for PERK/EIF2α signalling analysis of ER stress markers. The relative protein levels are shown. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6). *P < 0.05 versus sicontrol or TM group or versus WT group. β‐Actin was used as an internal control for normalizing the mRNA and protein levels. (f, g) Four‐month‐old obese FXR−/− mice were kept on a HFD in the presence and absence of betulinic acid (100 mg·kg−1·day−1) for 6 weeks. Livers from mice were harvested and stained with HE and Oil Red O. Scale bars, 100 μm (f). Relative mRNA expression of hepatic Chop and Bip. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6). *P < 0.05 versus vehicle or FXR−/− group. β‐Actin was used as an internal control for normalizing the mRNA and protein levels (g). (h) The schematic of th epharmacological mechanism by betulinic acid
