Figure 9.
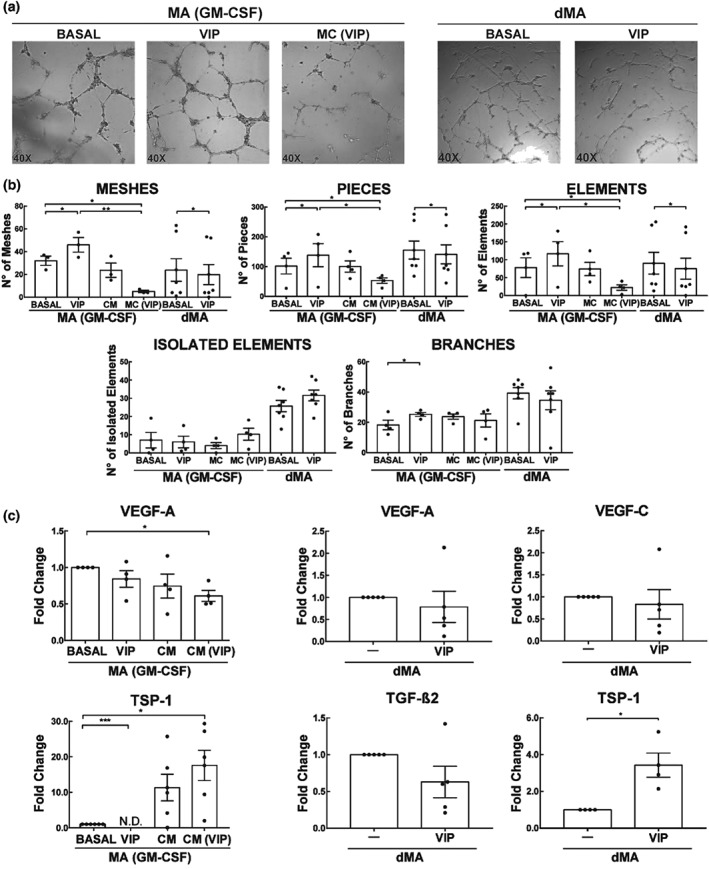
Effect of VIP on EC tube formation by dMA or trophoblast conditioned‐macrophages (GM‐CSF). (a) 2 × 104 EC were cultured for 8 hr in a Geltrex matrix with different treatments. Representative microphotographs of tube formation by macrophages (GM‐CSF) ± 100 nM VIP, CM or CM (VIP), and dMA treated or not with 100 nM of VIP. (b) Parameters obtained from Angiogenesis Analyser, ImageJ. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM of the number of the parameter (meshes, pieces, elements, isolated elements, and branches) in macrophages (GM‐CSF; n = 5) and dMA (n = 8). *P < 0.05. Friedman test and post hoc Dunn's test for macrophages (GM‐CSF) and Mann–Whitney for dMA were used to compare the results. (c) Pro‐ or anti‐angiogenic genes expression analysis in macrophages (G‐CSF) and dMA. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of arbitrary units (A.U.) *102, when Ct values were detected, when they were not (N.D.; n = 5). *P < 0.05. Friedman test and post hoc Dunn's test for macrophages (GM‐CSF) and Mann–Whitney for dMA were used to compare the results. CM: conditioned medium; dMA: decidual macrophages; EC: endothelial cells; MA: macrophages; VIP: vasoactive intestinal peptide
